|
|
2011-2012 Catalog [ARCHIVED CATALOG]
Course Descriptions
|
|
Key to Course Descriptions
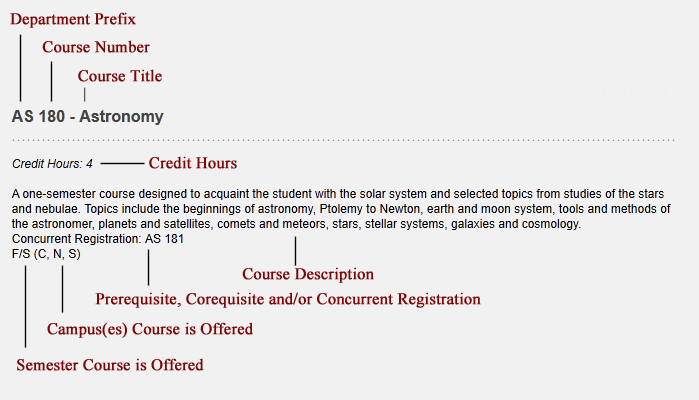
Abbreviations
| (C) |
City Campus |
F/S |
Fall and Spring |
| (N) |
North Campus |
SS |
Summer Session |
| (S) |
South Campus |
F+ |
Offered every other Fall |
| F |
Fall |
S+ |
Offered every other Spring |
| S |
Spring |
N |
Non-Credit |
Course Renumbering
A significant number of courses have been renumbered as part of the State University of New York’s policies which promote student mobility, through transfer of academic credit, to other SUNY institutions. All courses should be numbered at the 100-200 levels. This listing references the course with its Old and New numbers which should aid students in their choice of courses to complete academic program requirements and faculty in their role as academic advisor.
Course Renumbering Master List |
| |
Biology |
| |
-
BI 221 - Laboratory for BI 220
Credit Hours: 1.5
Students use fruit fly, bacterial and fungal cultures to gain an understanding of genetic principles. Human cell cultures are extensively used for chromosome studies.
Concurrent Registration: BI 220
SS (S)
|
| |
-
BI 225 - Botany
Credit Hours: 3
An introductory course designed to provide a basic understanding of plant structure and function. Classification, morphology, life cycles and evolution of algae, fungi, mosses, ferns, pines and flowering plants are discussed. Special emphasis is placed on flowering plant functions such as photosynthesis, respiration and plant hormones.
Concurrent Registration: BI 226
F/S (C, S)
|
| |
-
BI 226 - Laboratory for BI 225
Credit Hours: 1.5
This lab emphasizes plant morphology and anatomy of both lower and higher plants. Lab experiments include work on plant anatomy and physiology, taxonomy and ecology.
Concurrent Registration: BI 225
F/S (C, S)
|
| |
-
BI 230 - Microbiology
Credit Hours: 3
This course deals with the microorganisms such as yeast, molds, viruses, protozoa and bacteria with emphasis on the study of bacteria. The anatomy, physiology, ecology, economic importance and pathogenicity of these microorganisms will be included. Classifications of these microbes and the diseases produced by these organisms will be studied. Immunity, antigen-antibody reactions, sterilization methods and methods for cultivation of microorganisms will be covered.
Prerequisites: Any college-level biology course including lab. BI 150-151 are recommended.
Concurrent Registration: BI 231
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BI 231 - Lab for BI 230
Credit Hours: 1
This lab will give students experience in methods of isolation and aseptic techniques as well as enabling them to identify the microbes in the world around them.
Concurrent Registration: BI 230
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BI 241 - Applied Physiology
Credit Hours: 3
An elective course for students in the health related professions. This course provides an understanding of the physiology of disease based on a detailed knowledge of normal physiology. Disorders of selected systems including cardiovascular, digestive, nervous, pulmonary, immune and renal will be discussed.
Prerequisites: BI 150, BI 152
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BI 254 - Anatomy of the Eye
Credit Hours: 2
A detailed study of the composition of the eye and its associated structures such as the orbit, lids, lachrymal apparatus and muscles will be explored. This course also includes study of the visual pathway.
F (N)
Reserved for Ophthalmic Dispensing students only.
|
| |
-
BI 255 - Physiology of the Eye
Credit Hours: 2
A study of visual function including information processing, photoreceptor function, color vision, binocular vision, ocular motility, ocular nerves, blood supply and ocular pharmacology will be discussed.
S (N)
Reserved for Ophthalmic Dispensing students only.
|
Biomanufacturing |
| |
-
BT 110 - Basic Laboratory Skills/Lab Notebook
Credit Hours: 1
Laboratory procedures designed to encourage development of basic laboratory skills in the use of laboratory glassware and pipettes, the preparation of solutions and reagents and the use of the analytical balance and spectrophotometer. Students must report results according to established procedures.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 111 - Aseptic Processing
Credit Hours: 1
Aseptic processes designed to understand basic microbiology as it applies to bio-manufacturing, behaviors and rules applying to work in a clean room environment, “gowning” procedures, as well as proper documentation will be discussed.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 112 - Bio-Safety
Credit Hours: 1
This course is designed to expose the student to the culture of bio- laboratory safety as it applies to the bio-manufacturing industry. Discussion of precautionary labels, material safety data sheets (MSDS), use of protective equipment, handling laboratory equipment, safe handling and storage/disposal of chemicals, and understanding/writing standard operating procedures will be covered.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 114 - Good Manufacturing Practices
Credit Hours: 1
This course reveals the history of the bio-manufacturing industry past, current and future practices. Good Manufacturing Practices relating to local industry workforce needs are discussed. GMP documentation and guidelines including laboratory processes, recording keeping, production of batch records, terminology will be covered.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 115 - Regulatory Compliance
Credit Hours: 1
This course emphasizes the regulatory requirements for implementing and maintaining a quality system to facilitate the production of a product in a safe and consistent manner. An understanding of the importance for maintaining a quality system and the effects that this system has on the successful launch of products to market and the overall success of a company.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 116 - Standard Operating Procedures
Credit Hours: 1
In this course, the student will work with standard operating procedures (SOP’s) and batch records (protocols or procedures). Documentation in a regulatory environment will be covered. The student will gain experience in the design of research protocols, maintenance of health records, and participation in validation training.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 117 - Biomanufacturing Seminar
Credit Hours: 1
Students attend and participate in discussions and evaluations of their internship. Identified problems in the field as they relate to students internship, are assessed and analyzed, and solutions are formulated. Student participation is paramount to this problem solving process. Students in this course are also introduced to job opportunities that are available to graduate biomanufacturing students.
Corequisites: BT 118
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BT 118 - Biomanufacturing Internship
Credit Hours: 4
This course offers students supervised involvement in an internship at local biomanufacturing facilities. Through industry participation and facilitation, the student is introduced to the industry’s practical setting. Students complete the 160-hour internship program applying the skills that have been learned during the first two semesters of the program.
Corequisites: BT 117
F/S (N)
|
Building Management and Maintenance |
| |
-
BM 101 - Safety of Tools, Equipment and Materials
Credit Hours: 3
Safety practices used in the HVAC/R industry are demonstrated and practiced. The proper care and use of tools and equipment used in the installation and service of HVAC/R systems are demonstrated and practiced. The various types of piping materials used in the HVAC/R systems are discussed. The different methods of joining piping are studied. Soldering and brazing techniques are also demonstrated and practiced. Equipment and tools used to evacuate, leak test and charge a refrigeration system are demonstrated and practiced.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 105 - Refrigeration Principles
Credit Hours: 3
An introduction to the fundamental principles of refrigeration and the refrigeration cycle. Students will study the components of the refrigeration system, including compressors, condensers, metering devices and evaporators to fully understand their operation and function within the system. System controls and refrigerant types will also be covered.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 120 - Electricity for HVAC/R
Credit Hours: 3
Students will study basis electrical theory, including voltage, current and resistance and the measurement of each. Electrical circuits and wiring diagrams will be studied with emphasis on those commonly used in HVAC systems. Students will study and learn how to read and interpret the electrical schematic of an HVAC unit. The concepts of the electrical operations of a motor will be introduced. Various control circuits and control voltages will be discussed. The electrical control boards commonly found in HVAC units will be introduced. The principles of electrical safety pertaining to the servicing of HVAC equipment will also be covered.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 130 - Building Systems I
Credit Hours: 3
A course providing an overview of residential and commercial structural systems found in urban settings. Major topical areas include common construction techniques, maintenance practices, safety standards, material selection, tool and equipment usage necessary for routine facilities operation.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 140 - Electrical Systems I
Credit Hours: 3
A course covering the basic residential and light commercial electrical systems. The course will utilize national electrical code for reference and application. All hands-on activities will allow students to work with various materials and control devices.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 142 - Refrigerant Handling Certification
Credit Hours: 1
This course will cover the materials necessary to pass the EPA Section 608 Universal certificate. Areas of study will include EPA sections 608, 609, of the clean air act and the Montreal and Kyoto Protocols. The course will also cover CFC’s, HCFC’s and HFC’s refrigerants, their handling and recovering procedures mandated by the EPA.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 180 - Applied Mathematics and Estimating
Credit Hours: 3
A course designed to introduce students to formulas, measurement, geometric and algebraic skills necessary to function in the building trades and facilities management field. The process involved in the development of a cost estimate using both manual and computer methods will be covered.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 181 - Budget Control and Estimating
Credit Hours: 4
A course covering various phases of the estimate budget control process and project management techniques. The class assignments will utilize the computer for cost of materials, labor, and equipment estimating as well as scheduling and budget control of new and renovated projects.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 200 - Techniques of Renovation and Restoration
Credit Hours: 3
A course concerned with renovation and restoration of a residential and commercial structure. Students will prepare and present concept designs, estimates and project scheduling. Other course topics will include property evaluation and inspection, budgeting, material selection, equipment and site management. Students will use software for scheduling and estimating for class projects.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 210 - Commercial Air Conditioning Systems
Credit Hours: 3
This course will cover the principles of air conditioning as applied to larger commercial equipment. The theory, installation and operations of air and water source heat pumps, gas and electric roof top units and make-up Air units will be reviewed. Ventilation, economizers and exhaust theory and practices will also be discussed.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 215 - Workplace Practicum
Credit Hours: 3
This course deals with basic workplace issues that a new technician may encounter when entering the workforce. Topics covered will include, workplace safety and hazards of the industry, EPA refrigerant handling requirements and guidelines for certification along with employer, employee and customer relations issues.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 225 - Energy Management
Credit Hours: 3
The course will consider energy conservation techniques in both residential and commercial facilities such as: hotels, schools, office buildings, industrial buildings, apartment complexes, resorts and recreational centers. Major emphasis will focus on conducting an energy audit and analysis for payback and the implementation of the energy measures. Building automation systems will also be discussed.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 231 - Building Systems II
Credit Hours: 3
A course in the study of commercial structural systems with emphasis on the structural types: heavy timber, masonry, structural steel and reinforced concrete. Examination of blueprints describing component parts, materials, symbols, views, and schedules will be covered. Lab activities will include hands-on use of various masonry products.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 237 - Building and Grounds Operations
Credit Hours: 3
A course that will emphasize operational aspects of property management. To achieve this objective, a series of building surveys will be conducted. These surveys utilizing computer application, will include planning, scheduling, inventory control, design techniques, and budget preparation. General topics will include space planning interior maintenance plan, four seasons exterior maintenance plan, disaster planning, security plan and hazardous material procedures.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 240 - Plumbing Systems
Credit Hours: 3
A course covering the fundamentals of design and layout of plumbing pipe, fittings, and fixture installation. Topics will include: supply and waste piping, sanitary and storm drain sewage disposal, air, oil, and gas lines. Also included: The installation and maintenance of residential/commercial systems of fixtures and hot water heaters.
Alternative energy conservation methods used for material usage, equipment and installation available to industry will be included for green technology used in facilities new and old today.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 241 - Electrical Systems II
Credit Hours: 3
A course covering commercial power, lighting distribution circuitry, HVAC controls and maintenance. Topics include the control circuitry utilized in HVAC equipment lighting systems and an overview of building automation systems and security systems utilized in many of today’s facilities.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 243 - Heating Systems I
Credit Hours: 3
A course covering the fundamentals of residential heating systems, distribution systems, and associated equipment. The installation, daily operations, and maintenance will be reviewed. Troubleshooting methods using the latest in diagnostic equipment, the high efficiency resdidential systems, their control systems, and latest material used for distribution systems will also be covered.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 244 - Air Conditioning and Ventilation
Credit Hours: 3
A course covering the fundamentals of refrigeration, air conditioning, ventilation and their principles. Topics include: system types, components, equipment, controls and troubleshooting procedures. The lab will utilize hands-on applications as well as computer simulations of air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 246 - Heating Systems II
Credit Hours: 3
A course reviewing HVAC systems and boilers commonly used in commercial facilities. The operating principles of heat pumps, their system components, as well as heating distribution systems. The course will also cover typical roof-top HVAC units, their system, distribution, controls, and diagnostic troubleshooting. Additional heating topics will include: low pressure boilers, their operations, boiler fittings, steam accessories, draft control, safety water treatment, and maintenance.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 250 - Renewable Energy Systems
Credit Hours: 4
This course will provide a student with a comprehensive working knowledge of practical applications for integration of renewable energy systems within commercial and residential building systems. These renewable systems would include photovoltaic (domestic hot water, space heating, and power generation); solar thermal (water heating, heating and cooling); geothermal (heating and cooling, domestic hot water); wind power (pumping of water, and power generation); as well as other emerging technologies (fuel cells, biofuels, ECT) will be introduced. Mechanical systems within existing structures using traditional energy sources will be reviewed for both conservation opportunities and potential renewable integration. The systems overview will employ traditional lecture/demonstration methods with relevant case studies along specified hands-on simulated lab activities.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 255 - Green Building Technology
Credit Hours: 3
The primary emphasis of this course will be to provide the participants with an understanding of green, clean and sustainable technologies; tool and equipment usage as they relate to site selection, building design and adaptive reuse; construction methods; material selection– new, alternative, reclaimed & traditional; cost estimation; conservation techniques – site, water, materials, construction waste, energy & building design; system interaction & integration; and building environmental quality.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 260 - Electrical Systems for Renewable Energy
Credit Hours: 3
This course will provide the student with the ability to identify diverse methods of alternative electrical energy production, and the positive and negative aspects of each. Some of the technologies that will be discussed and troubleshot are wind energy, passive and photoelectric energy, nuclear energy, hydroelectric energy, biomass and alternative fuel vehicles. The advantages of using various alternative energy technologies, the effects or by-products of each and the problems that the technician may encounter will be covered.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 266 - Green HVAC & Plumbing
Credit Hours: 3
The primary focus of this course is to provide the students with the knowledge and practical experience necessary to install, maintain and troubleshoot mechanical systems. Many of the green sustainable systems will utilize traditional technology with alternative energy sources for power. Students will learn concepts of water conservation methods for distribution systems and fixtures which will enable them to gain practical experience with plumbing and heating systems and then fluid distribution systems. Students will learn concepts of conservation methods of water for both fixture and distribution selection.
F/S (C, N)
|
| |
-
BM 270 - Project Management
Credit Hours: 2
A course to organize, plan and develop a facility’s daily operations. Students will develop a mission statement and objectives for maintenance functions. Software for planning of activities for maintenance of facilities will also be a major topic.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 272 - Property Management
Credit Hours: 3
A course designed as an introduction to the field of property management. The course covers operations and marketing techniques for specialized properties. Topics covered include contract leases, management agreements, public relations, budgets, economic trends, financial analysis, contractor selection, compliance issues, maintenance, and marketing.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 275 - Maintenance Management/Supervision
Credit Hours: 3
A course designed as an introduction to supervision. The course addresses applications to the specific concerns of facilities professionals. Topics include long and short range planning, scheduling techniques, organizing and delegating work, labor relations, human psychology, problem solving, decision making, TQM, customer service, compliance, and supervising employees. The course is designed to train students to be first level supervisors.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 281 - Facilities Maintenance & Environmental Topics
Credit Hours: 3
A course designed as an introduction to the fundamental operating principals, maintenance and troubleshooting for a variety of mechanical and electrical systems found in Facilities and Industry. Maintenance management is featured through the application of preventative and predictive maintenance. Systems studied include computerized maintenance management (CMMS); safety; service & repair principles; electrical, electronic and programmable controllers; refrigeration; boilers; HVAC; mechanical; fluid power and troubleshooting.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BM 290 - Maintenance Programs
Credit Hours: 4
A capstone course that will allow students to set up a complete preventative maintenance program using all the preceding course contents combined, with observations made at site. Computer software applications will be used by students to develop a preventative maintenance program and associated reports.
S (C)
|
| |
-
BM 295 - Green Building Lab
Credit Hours: 3
The laboratory course will offer students a holistic approach that integrates green sustainable building techniques with renewable energy systems. The Green Building Practical Laboratory is designed to provide students with realistic hands-on activities. The skills and knowledge that was gained by students in preceding courses will be reinforced at our cooperative green building worksite.
F/S (C, N)
|
Building Rehabilitation |
| |
-
BR 100 - Building Trades Restoration Practicum I
Credit Hours: 4
An introductory course designed to help the student analyze the problems and related solutions in a rehabilitation project. Topics covered would be removal of existing interior finish materials, insulation techniques, rewiring, window replacement, plumbing replacement, drywall installation and repair paneling, painting, staining, and finishing techniques.
F (C)
|
| |
-
BR 102 - Building Trades Restoration Practicum II
Credit Hours: 4
A continuation of BR 100, further developing interior finishing techniques considering restoration techniques. Other topics will include maintaining exterior finish materials, replacement of exterior windows and doors, and maintaining roofing materials. Course to be offered at a building site.
Prerequisites: BR 100
S (C)
|
Business Administration |
| |
-
BU 120 - Introduction to Accounting
Credit Hours: 3
This is a course with dual emphasis. It acclimates the student to accounting principles starting with the journal and ending with the balance sheet and income statement. It also acts as a refresher course as it deals with the in-depth mathematical calculations involved in financial accounting.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 121 - Accounting Principles I
Credit Hours: 4
A comprehensive study of the basic elements of accounting with the completion of a practice set of books for a representative business concern including cost receipts and payments, payroll, petty cash, purchases and sales records, accounts receivable, operational assets, accounts payable and the preparation of a financial statement, with a laboratory period at the option of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 122 - Accounting Principles II
Credit Hours: 4
A continuation of principles, including such topics as partnerships and corporate accounting, manufacturing accounting and budgeting, with a laboratory period at the option of the instructor.
Prerequisites: BU 121 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 130 - Quantitative Business Methods
Credit Hours: 3
Practical applications in typical business problems involving interest and discount computations and wage and tax calculations, as well as determining depreciation, insurance premiums, real estate rates and financial statement ratios.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 131 - Computer Applications in Business
Credit Hours: 3
An introductory course in essential state of-the-art business related computer skills. Topics include, but are not limited to, terminology, computer equipment, machine capabilities and limitations, current popular business software and its application to realistic business problem solving in areas such as finance, marketing and accounting. No prior computer or business experience required.
F/S (C, N, S)
No prior computer or business experience is required.
|
| |
-
BU 140 - Introduction to Business
Credit Hours: 3
Analysis of business structure, management, functions and governmental influence. Review of economic thought and influence on commercial business. Introduction to the terminology of business administrators; surveys the relationship of business to social environment and how each influences the other.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 151 - Principles of Marketing I
Credit Hours: 3
A survey of the basic marketing structure in a private enterprise economy. A consideration of the economic, sociological, psychological and political factors that make up the environmental setting. The various means and methods of moving goods from producer to ultimate consumer will be studied.
Prerequisites: BU 140 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 221 - Computerized Accounting
Credit Hours: 4
The purpose of this course is to teach the latest technology in computerized accounting that is currently being utilized by business. The basic elements of accounting will be used such as general ledger, payroll, accounts receivable, accounts payable, inventory and invoicing.
Prerequisites: BU 120 or BU 121 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 222 - Intermediate Accounting I
Credit Hours: 3
A detailed study and analysis of the balance sheet accounting, with particular emphasis on assets, analysis of receivables, inventory costing and valuation problems.
Prerequisites: BU 122 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 223 - Intermediate Accounting II
Credit Hours: 3
A continuation of the detailed study of balance sheet accounts, including concentration on liabilities, stockholder equity, retained earnings and flow of funds.
Prerequisites: BU 222 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 224 - Cost Accounting
Credit Hours: 3
A study of manufacturing accounting, including consideration of the job cost, process cost and standard cost systems, as well as the problem of costing joint products and by-products.
Prerequisites: BU 122 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 225 - Introduction to Income Tax
Credit Hours: 3
A study of the current federal and state regulations with an opportunity for practical application in the preparation of individual, partnership and corporate returns.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 226 - Managerial Accounting
Credit Hours: 3
An explanation of the interpretation and use of accounting data by management in developing budgets, planning, cost and profit analysis.
Prerequisites: BU 122 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 231 - Business Systems
Credit Hours: 3
The course is designed to be an introduction to the theory and practice related to the development and operation of information systems in organizations. Emphasis will be placed on the development and management of information systems. Applications, techniques and tools involved in management information systems, such as the processing of data and information via computers will be discussed and/or used.
Prerequisites: BU 131 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 232 - Business Finance
Credit Hours: 3
Typical financial problems involved in the establishment and operation of business organizations with emphasis on the corporate form. Such topics as corporate securities, long and short-term financing, budgeting, taxation, distribution of earning, credit collections and receivables financing will be considered.
Prerequisites: BU 122 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
May require the use of computers.
|
| |
-
BU 233 - Consumer Finance
Credit Hours: 3
A general interest course designed to help the individual better understand the financial world in which we live today. Topics will enhance one’s ability to make personal financial decisions which will include establishing an individual’s financial goals, making decisions on saving money, making investments, buying a car, acquiring insurance and budgeting. This course is designed to benefit all and therefore, no prior business training is required.
F/S (C, N, S)
This course is to be used as an open college elective for non-business majors. Courses may include the preparation of personal financial software.
|
| |
-
BU 234 - Investments
Credit Hours: 3
The study of investment principles, including their objectives, approaches to meeting objectives, the mechanics of investments, securities and market operations.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 240 - Principles of Management
Credit Hours: 3
A study of management processes including supervision, operational control, labor relations and personnel selection. Coordinating, motivating and controlling techniques, as well as decision making functions will be studied.
Prerequisites: BU 140 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 241 - Organizational Behavior
Credit Hours: 3
This course focuses on the internal control of the organization with respect to motivation, leadership and job satisfaction. Using these concepts as a perspective and foundation to an underlying premise that organizational behavior overlaps with organization theory, design and behavioral control systems. Critical analysis will show that management must, through design, planning and control of these functions and their relations to one another effectively maintain the organization to operate with maximum efficiency, profitability and employee satisfaction.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 242 - Human Resource Management
Credit Hours: 3
A course of study which will consider characteristics, purposes, objectives and techniques of supervising and coordinating the work of others. Topics such as interview and training procedures, human relations, current policies and legislation affecting labor management relations will be considered.
Prerequisites: BU 140 or department waiver.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 243 - Entrepreneurship
Credit Hours: 3
An analysis of the various risks involved in starting and managing a small business concern, including planning, organizing, financing, budgeting, marketing and management control. The student will develop an understanding of the economic and social environment within which small concerns function by providing the practice needed for decision making under conditions of uncertainty. The applications of the above functions in retailing, franchising, service industries and manufacturing will also be explored.
Prerequisites: BU 140, BU 151, BU 240
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 244 - Introduction to Sports Management
Credit Hours: 3
An investigation of the scope of the sport industry. Functions of management, skills and attributes required of a sport manager and roles of a manager are discussed. Attention focused on how the managerial process relates to sport organizations and their products. Students will become acquainted with career opportunities in the sport management field.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BU 245 - Administrative Practices in Sports Management
Credit Hours: 3
This course covers organization and administrative policies, standards and procedures for managing a business in the sport industry. Includes topics such as management functions related to sports, business structure formation, employment issues, risk management and legal liability.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
BU 247 - Business Plan Completion
Credit Hours: 3
This course, normally based on a computer software package, permits the student to prepare a good form business plan for a business he or she would like to initiate. The student must prepare an executive summary, as well as marketing, management and financial plans, in a format acceptable for filing with the Small Business Administration and with local banks.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 248 - Practicum in Supervision
Credit Hours: 3
The purpose of this course is to develop higher levels of management and supervisory skills based on current techniques of motivation, leadership and conflict resolution. The practicum will use a case problem and critical-incident method whereby students are asked to make personnel decisions based on their knowledge of Title VII, EEOA, Nora and other important federal and new York statutes. Issues covered will include strikes, discrimination, unfair labor practices and the grievance practices.
Prerequisites: BU 140 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 251 - Principles of Marketing II
Credit Hours: 3
This course builds upon the basic concepts and practices introduced in Principles of Marketing I - BU 151. It will provide a firm understanding of how to define and segment a market, how to develop product and services for chosen target markets, how to price offerings to make them attractive and affordable and how to develop a promotional mix in order that customers will be aware of and desire a firm’s products.
Prerequisites: BU 151 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 252 - Marketing Management
Credit Hours: 3
This course is a study of the organization, planning and operation of the marketing department. It includes coordination, supervision and personnel selection.
Prerequisites: BU 151 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 253 - Retailing
Credit Hours: 3
This course will cover the principles and practices unique to retailing—a branch of business directly related to the public, trends and philosophy. The course will feature the steps in conceptualizing, preparing for and planning a small retail business.
Prerequisites: BU 151 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 254 - Advertising
Credit Hours: 3
A general study of the procedures and techniques, including determination of objectives, idea brainstorming, writing copy, planning layout, selecting media and utilizing research.
Prerequisites: BU 151 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 255 - Salesmanship
Credit Hours: 3
A study of the fundamentals of successful selling, including prospective buyer motivation, the approach, varying techniques and the closing. Film, tapes and record demonstrations will be utilized with student presentations.
Prerequisites: BU 151 or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 261 - Business Law I
Credit Hours: 3
A survey of legal principles often encountered in business. Consideration is given to judicial procedures, torts, crimes, contracts, insurance, real property and negotiable instruments.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 262 - Business Law II
Credit Hours: 3
A survey of legal principles often encountered in business. Consideration is given to wills and inheritance, sales, secured transactions, agencies, partnerships and corporations and the general legal environment in which business operates.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 271 - Internship
Credit Hours: 3
The internship course is designed to provide realistic training in the field of business by providing on-the-job experience consisting of approximately 135 hours of supervised activity for an appropriate business firm, institution and/or agency. This work experience, along with the academic program, will enrich the theoretical concepts developed in the classroom and enable the student to prepare for entrance into a competitive work environment. Additionally, the internship may connect students to employment opportunities and will create a bond between the student, the college and the business community. Although many internships are non-paid experiences, students may receive remuneration for their work.
Prerequisites: Permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 272 - Cooperative Education - Business Administration
Credit Hours: 3
Cooperative Education provides business majors an opportunity to earn credit toward a degree by working at a job related to their college major or career interest. Students take a career related classroom seminar (50 min. per week) while working at a job (approximately 165 hours per semester) in the area of business administration.
Prerequisites: 2.5 GPA; Completion of at least 24 credit hours of college work (including sufficient academic credits in major area of study to be marketable to an employer); permission of the appropriate department chairperson.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BU 295 - Special Business Topics
Credit Hours: 3
An examination of current problems in business organized on a lecture/ discussion basis. The content of the course will vary as changing conditions require the use of new approaches to deal with emerging problems.
Prerequisites: Senior standing or permission of the instructor.
F/S (C, N, S)
This may often be a capstone course.
|
Chemistry |
| |
-
CH 010 - Preparatory Chemistry
Credit Hours: 3 Not for degree credit
A preparatory course for students who will take CH 140, CH 144, CH 146, CH 180. Topics include: scientific method, states of matter, atoms, elements, compounds, the periodic table, formulas and nomenclature, equations, metric system, dimensional analysis and mole concept.
Concurrent Registration: CH 011
F/S (C, N, S)
Since this is a noncredit course, it cannot be applied toward an associate’s degree.
|
| |
-
CH 011 - Lab for CH 010
Credit Hours: 1.5 Not for degree credit
This preparatory course assumes no prior laboratory experience. Emphasis is placed on experimental procedures, manipulations, techniques, data gathering and data evaluation. Experiment topics may include classification, use of balances, determination of density, filtration, flame tests, odors, chemical reactions, melting and boiling points, air pollution, organic chemistry, gas laws and biochemistry.
Concurrent Registration: CH 010
F/S (C, N, S)
Since this is a noncredit course, it cannot be applied toward an associate’s degree.
|
| |
-
CH 110 - Survey of Science
Credit Hours: 3
An introductory science course surveying basic topics in chemistry, physics, biology, earth science and astronomy. This course will serve as a science elective for non-science majors; science majors may take it as a general elective.
F/S (N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 112 - Understanding Drugs
Credit Hours: 3
A course dealing with the makeup and effects on the body of a variety of common drugs including pain relievers, narcotics, barbiturates, hallucinogens and antibiotics. This course will serve as a science elective for non-science majors; science majors may take it as a general elective.
F/S (N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 114 - Chemistry for Consumers
Credit Hours: 3
A terminal course for non-science majors which provides explanations of the chemistry observable in the household, the environment and the news.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 007 or MT 013, English Placement EN 110 or EN 120 (reading)
F (N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 116 - Chemistry and the Environment
Credit Hours: 3
A discussion course designed for non-science majors. Topics will include energy concerns, the pollution crisis, natural resources and human interaction with the environment. Science majors can take the course as a general elective only.
Prerequisites: English Placement EN 110 or EN 120 (reading)
F/S (N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 118 - Forensic Science
Credit Hours: 3
A liberal arts elective in which the basic principles underlying the science of chemistry will be applied to an understanding of criminal investigative techniques. General chemical techniques used in criminal investigations from the gathering of evidence to the final presentation of expert testimony will be discussed.
F/S (C)
|
| |
-
CH 140 - College Chemistry I
Credit Hours: 3
An introduction to chemistry designed primarily for those students who have little background in the subject but whose curriculum requires a working knowledge of chemistry. Topics include mathematics fundamentals, atomic theory, periodic table, chemical bonding and nomenclature, chemical equations, stoichiometry and gas laws. Satisfies science requirements for all but liberal arts-science students.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 007
Concurrent Registration: CH 141
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 141 - Lab for CH 140
Credit Hours: 1.5
Topics covered: measurement, physical properties, specific heat and atomic weight, synthesis and gravimetric analysis of compounds, chemical reactions and molecular weight determination of gases. This course satisfies the science requirements for all but liberal arts-science students.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 007
Concurrent Registration: CH 140
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 142 - College Chemistry II
Credit Hours: 3
Continuation of CH 140. Topics include solutions, acidimetry, alkalimentry, oxidation- reduction, reaction rates and chemical equilibrium, organic chemistry, metals and polymers and bio-chemistry.
Prerequisites: CH 140
Concurrent Registration: CH 143
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 143 - Lab for CH 142
Credit Hours: 1.5
Continuation of CH 141. Topics covered: solutions, acid and base titration, redox analysis, pH indicators, introduction to organic compounds and qualitative analysis of transition metal cations.
Prerequisites: CH 141
Concurrent Registration: CH 142
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 144 - General Chemistry with Introductory Organic and Biochemistry
Credit Hours: 3
A one-semester course intended for students in the health science fields whose career objective requires knowledge of broader applications of chemistry. The course covers the fundamental concepts and essentials of general chemistry, introductory organic chemistry and an introduction to biochemistry.
Prerequisites: High school chemistry or CH 010
Concurrent Registration: CH 145
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 145 - Lab for CH 144
Credit Hours: 1.5
Topics include: metric system of measurement, reactions in solution, colloidal dispersion, gas laws, acidity and its determination, organic synthesis and biochemical reactions.
Prerequisites: High school chemistry or CH 011
Concurrent Registration: CH 144
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 146 - College Chemistry with Clinical Applications
Credit Hours: 3
A rigorous, science majors’ general chemistry course slanted toward medical laboratory applications. Topics covered: atomic structure, chemical bonding, reaction types and equations, stoichiometry, equilibrium, acid-base theory, pH, Henderson-Hasselbalch equation and introduction to organic chemistry.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 125 and high school chemistry or CH 010 and CH 011
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
CH 180 - University Chemistry I
Credit Hours: 3
The first course of a two-course sequence; detailed introduction to chemistry for science, engineering, or health-related majors. Example topics include: dimensional analysis, chemical nomenclature, states and classes of matter, atomic theory, quantum theory, gas laws, chemical equations and stoichiometry, periodicity, chemical bonding, thermochemistry.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 125 (or higher) and high school (Regent’s) chemistry or CH 010
Corequisites: Ch 181
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 181 - Lab for CH 180
Credit Hours: 1.5
Topics include: laboratory techniques, physical properties, use and care of analytical balance, gravimetric determinations, gas laws, molecular weight determinations, solubility and fractional crystallization, chromatography, vapor pressure, heat of vaporization and thermochemistry.
Prerequisites: Math Placement MT 125 (or higher) and high school (Regent’s) chemistry or CH 011
Concurrent Registration: CH 180
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 182 - University Chemistry II
Credit Hours: 3
The second course of a two-course sequence; detailed introduction to chemistry for science, engineering, or health-related majors. Example topics include: intermolecular forces, colligative properties, chemical kinetics, equilibria, thermodynamics, electrochemistry, nuclear chemistry, and organic chemistry.
Prerequisites: CH 180
Corequisites: CH 183 (lab) is highly recommended as a co-requisite.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
CH 183 - Lab for CH 182
Credit Hours: 1.5
Molecular weight by freezing point depression, electrochemistry, volumetric analysis, equilibrium constant determination, rates of reaction and qualitative analysis.
Prerequisites: CH 181
Concurrent Registration: CH 182
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
Page: 1
| 2
| 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
… Forward 10 -> 14 |
|
|