|
|
2020-2021 Catalog [ARCHIVED CATALOG]
Course Descriptions
|
|
Key to Course Descriptions
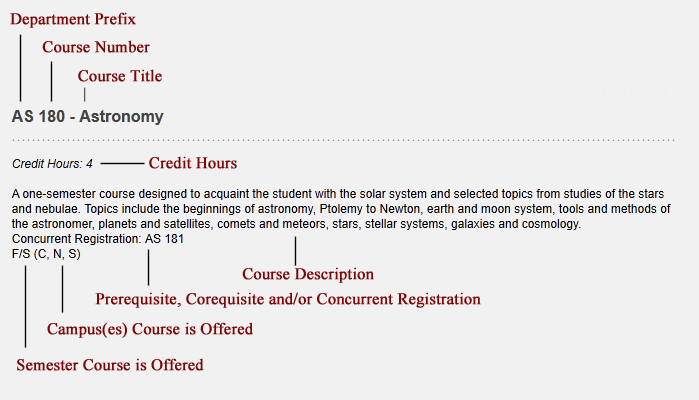
Abbreviations
| (C) |
City Campus |
F/S |
Fall and Spring |
| (N) |
North Campus |
SS |
Summer Session |
| (S) |
South Campus |
F+ |
Offered every other Fall |
| F |
Fall |
S+ |
Offered every other Spring |
| S |
Spring |
N |
Non-Credit |
Course Outlines
Course outlines for all courses described in this catalog are available for viewing. To explore the general framework of a course design and view the expectations of student performance within a select course click on the link below. These descriptions provide the base upon which instructors build their own course syllabi for the individual sections offered by the academic departments. Individual sections may therefore vary somewhat from the descriptions given in the outlines.
Course Outlines
|
| |
Physical Education |
| |
-
PE 125 - Fundamentals of Intercollegiate Athletics IV
Credit Hours: 1
A course that focuses on athletic and personal development in selected intercollegiate sports. Current participation on a college sports team is required.
Course Outcomes
At the end of this course, a successful student will possess the ability to:
- pass a skill test based on the particular sport and position played; and
- participate on a sports team as a student-athlete.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 130 - Introduction to Sailing
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory course designed to teach fundamental sailing skills and basic sailing concepts through a combination of classroom and sailing activities.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion, the successful student will be able to:
- define the points of sailing;
- explain the physical principles of sailboat movement;
- explain the principles of air movement over sails and proper sail trim to maximize lift; and
- demonstrate the ability to sail on a “reach”.
F (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
PE 145 - Exercise Science Practicum
Credit Hours: 2
A course designed to provide students with an opportunity to observe professionals working in the field. Students will select a setting in the health and wellness field where they will be under the direct supervision of a professional (i.e. exercise physiologist, physical therapist, physician, physical educator, chiropractor, personal trainer, etc.) at various public, private or therapeutic agencies. Prerequisites: First Aid certification, PE 109, PE 142, PE 143 or by permission of instructor only.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe duties and scope of practice of a professional in a health and wellness career; and
- observe professionals applying knowledge and skills applicable to careers in health and wellness.
Prerequisites: PE 109, PE 142, PE 143 or permission of the instructor
F/S (N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 180 - Exercise Nutrition
Credit Hours: 3
This course addresses the unique nutritional considerations of physically active individuals and athletes. Course topics will include the newest information on energy metabolism, macronutrient and micronutrient needs, nutritional supplements, body composition and special considerations for a variety of exercising populations including children, master athletes and strength/endurance trainees. Exercise professionals such as coaches, personal trainers, physical educators, athletic trainers, exercise specialists, as well as, individuals who participate in sports and exercise activities will benefit from this course.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- explain nutrition needs of various exercising populations;
- recommend fluid requirements for athletes, before/during/after exercise to maintain hydration;
- explain different methods designed to assess body composition;
- explain relationship between body composition, health and athletic performance;
- assess scientific evidence of common nutritional practices in the sport setting;
- identify situations in which nutritional information should be provided to clients within the scope of practice of non-nutrition professionals;
- describe energy systems, fuels and nutrients supporting physical activity; and
- assess diets and identify nutrition and caloric recommendations for exercising individuals using dietary analysis tools and resources.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 200 - Physical Education I
Credit Hours: 1
A class which introduces students to the basics of being a physically educated person. Proper techniques will be presented and practiced which will help students improve their skill level. Knowledge about the rules, keeping score, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized. The specific activities will be chosen by the instructor.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- evaluate performance, identify rules, and activity etiquette;
- demonstrate fundamental skills of the activity; and
- apply basic strategy during performance or game play.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 201 - Physical Education II
Credit Hours: 1
A class which introduces students to the basics of being a physically educated person. Proper techniques will be presented and practiced which will help students improve their skill level. Knowledge about the rules, score keeping, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized. Specific activities will be selected by the instructor.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- evaluate performance, identify rules, and etiquette of the activity;
- demonstrate fundamental skills of the activity; and
- apply basic strategy during performance or game play.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 202 - Physical Fitness I
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory class emphasizing the development of an individualized fitness program. Students will engage in a variety of activities while gaining knowledge of the health-related components of physical fitness to improve their overall fitness level. Students will focus on reaching the standards for entrance into the NYS police academy http://nytrooper.com/physical ability test.cfm and http://nytrooper.com/fitness levels.cfm.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- identify the physical benefits of an active lifestyle;
- describe the five health-related components of physical fitness;
- demonstrate measured improvements in cardiovascular, muscular strength and flexibility; and
- design and implement a personal fitness program to meet personal goals.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 203 - Physical Fitness II
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory class emphasizing the development of an individualized fitness program. Students will engage in a variety of activities while gaining knowledge on how to apply the FITT principles to improve their overall fitness level. Students will focus on reaching the standards for entrance into the NYS police academy http://nytrooper.com/physical ability test.cfm and http://nytrooper.com/fitness levels.cfm.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- apply the FITT principles to the components of physical fitness;
- demonstrate measured improvements in cardiovascular, muscular strength and flexibility; and
- design and implement a personal fitness program to meet personal goals.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 206 - Basketball
Credit Hours: 1
This introductory class develops fundamental basketball skills; such as: dribbling, passing and shooting. Knowledge about the rules of the game, court strategy, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- identify the rules, court and etiquette of basketball;
- demonstrate basic fundamental skills of basketball: dribbling, passing and shooting; and
- apply basic offensive and defensive strategy during game play.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 207 - Aerobics
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory class designed to teach students the basic knowledge of aerobics. Students will engage in aerobic dance which gives the body a total fitness workout including cardio respiratory endurance, muscular strength, muscular endurance, balance and flexibility. Areas to be covered include safety guidelines, fitness training principles and a variety of training methods for aerobic fitness. Students should develop an appreciation for fitness and have adequate information to form a base for starting and continuing a lifetime fitness program.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- identify basic aerobic dance moves by matching the move with the corresponding name for the move;
- demonstrate proper technique for basic aerobic dance moves;
- demonstrate improved endurance by being able to perform vigorous, nonstop movement;
- demonstrate improved coordination and rhythm by being able to perform the dances taught in class;
- develop a personal fitness program; and
- evaluate a classmate’s skill level performing basic aerobic dance moves.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 208 - Volleyball
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory class emphasizing the development of the fundamental volleyball skills: passing, setting, hitting, blocking, digging and serving. Knowledge about the rules of the game, court strategy, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify the rules and etiquette of volleyball;
- demonstrate basic fundamental skills of volleyball: passing, setting, hitting, blocking, serving, etc;
- apply basic offensive and defensive strategy during game play; and
- evaluate a classmate’s skill level: passing, setting, and serving.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 213 - Bowling
Credit Hours: 1
Class will introduce students to the basics of bowling. Proper bowling techniques will be presented and practiced to help students improve their game. Knowledge about rules, score keeping, lane strategy, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- keep score, identify rules, and use proper bowling etiquette;
- demonstrate fundamental skills, safety, and techniques of bowling; and
- demonstrate knowledge of bowling terminology.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
-
PE 215 - Yoga II
Credit Hours: 1
A course designed to teach the student a variety of yoga postures and yoga breathing techniques to help contribute to their overall fitness, with an emphasis on stretching the muscles and strengthening the body’s core.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the eight limbs of Yoga;
- describe the benefits of a daily yoga practice;
- demonstrate 25 basic/advanced yoga poses; identify muscles involved, benefits, proper alignment and integration of the breath while coming into and out of the pose;
- describe the importance of and demonstrate the complete breath, diaphragmatic breathing, 2:1 breathing and alternate nostril breathing; and
- describe and demonstrate the benefits of focus and quieting the mind.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 220 - Physical Education III
Credit Hours: 1
A class which introduces students to the basics of being a physically educated person. Proper techniques will be presented and practiced which will help students improve their skill level. Knowledge about the rules, score keeping, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized. Specific activities will be chosen by the instructor.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- evaluate performance, identify rules, and etiquette of the activity;
- demonstrate fundamental skills of the activity; and
- apply basic strategy during performance or game play.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 221 - Physical Education IV
Credit Hours: 1
A class which introduces students to the basics of being a physically educated person. Proper techniques will be presented and practiced which will help students improve their skill level. Knowledge about the rules, score keeping, skill assessment and teamwork will be emphasized. Specific activities will be selected by the instructor.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- evaluate performance, identify rules, and etiquette of the activity;
- demonstrate fundamental skills of the activity; and
- apply basic strategy during performance or game play.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 222 - Cooperative Games
Credit Hours: 1
This is an activity course in which students will learn how to develop group cohesion while participating in personal and group problem solving initiatives games, trust activities and cooperative games. Students will see firsthand the synergy that can be created within their group by accomplishing seemingly menial tasks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate and follow the proper safety protocols for trust and other activities utilized in class; and
- assess and present cooperative activities to a group of students.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 223 - Weight Training I
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory class emphasizing the development of an individualized weight training program. Students will engage in a variety of strength and endurance training activities, while gaining knowledge about the importance of muscular fitness for a healthy lifestyle.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- identify major muscle groups and their function;
- demonstrate the proper techniques of weight training; and
- exhibit measured improvements in muscular strength and endurance.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 224 - Weight Training II
Credit Hours: 1
A class emphasizing the development of an individualized weight training program. Students will engage in a variety of strength and endurance training activities, while gaining knowledge about the importance of muscular fitness for a healthy lifestyle.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- Identify major muscle groups and their function.
- Demonstrate the proper techniques of weight training.
- Exhibit measured improvements in muscular strength and endurance.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 225 - Introduction to Coaching Sports
Credit Hours: 3
A course designed to educate individuals interested in becoming a certified coach in various sports. This will be accomplished by fostering an understanding of the sport rules and strategy while learning how to develop practice plans. Career opportunities in high school or college athletics, as well as knowledge in eligibility will also be covered.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe how to become a certified coach in New York State;
- identify career and professional development possibilities;
- develop a daily, weekly and seasonal practice plan for a sport season; and
- demonstrate knowledge in the area of eligibility in high school/college athletics.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 240 - Exercise Physiology with Lab
Credit Hours: 4
This course studies the body’s acute and chronic physiological responses to physical activity. Adaptations of body systems to physical activity such as cardiovascular, respiratory, neuromuscular, metabolic, hormonal etc. will be studied. In addition, the effects of physical activity will be examined considering different work intensities, gender, age, environmental conditions, etc. Students will study the foundations for the field of exercise physiology and the contributions of research to the discipline.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the origin of the discipline of exercise physiology, current professional organizations and applied research in the field;
- using case studies, conduct an exercise test and identify normal/abnormal responses to exercise and deduce acute and chronic physiological adaptations associated with physical activity;
- explain the effects of gender, age, environmental conditions, level of training, etc. on exercise responses;
- have knowledge of bioenergetics in physical activity including how muscle tissue generates energy, sources that provide energy, and energy requirements of diverse physical activities. Measure energy expenditure at rest and exercise using a metabolic cart;
- identify and recognize physical activities that will provide a training effect to the aerobic/anaerobic energy systems, musculo-skeletal system, cardio-respiratory system and optimize physical performance;
- discriminate between the positive and negative health benefits of a variety of physical activities; and
- assess body composition using a variety of methods. Distinguish the relationship of nutrition and exercise performance, and the effects of physical activity on weight control.
Prerequisites: EN 110
F (N,S)
|
| |
-
PE 250 - Football
Credit Hours: 1
This course is designed to introduce students to the concepts, strategies and skills associated with American Football. Emphasis will be placed on skill development and participation as a member of an in-class football team. This is a non-contact class; students will participate in games of flag football.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- understand and discuss the rules, strategies and positions associated with flag football;
- understand and implement proper safety measures while playing and/or teaching flag football;
- demonstrate the skills necessary to participate effectively in a flag football game; and
- utilize the Sport Education Model to participate as a member of an in-class football team.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 252 - Intermediate Bowling
Credit Hours: 1
A class where bowling skills are developed and refined. Proper bowling techniques and etiquette will be presented and practiced, which will help students improve their game. Emphasis will be on skill refinement.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- refine skills using correct bowling form and technique;
- evaluate and correct errors in bowling form and execution; and
- outline teaching progressions for bowling skill development.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 253 - Advanced Bowling
Credit Hours: 1
This course will focus on the development of a competitive bowler, emphasizing the refinement of advanced bowling skills.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- develop/possess skills at the level of a competitive bowler;
- articulate various competitive strategies relative to bowling; and
- outline a year-round personal training program for the competitive bowler.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PE 255 - Sports & Leisure Studies Practicum
Credit Hours: 2
This course is designed for upper level students to interact with professionals currently working in the field of Sports and Leisure Studies. Students will observe professionals in an authentic setting, develop professional contacts and references, and utilize skills and theory learned in the classroom.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe and outline the duties and responsibilities of the Sports & Leisure professional they observed;
- navigate a professional workplace environment;
- apply reflection(s) to enhance professionalism and professional skill set(s) required in the workplace; and
- add observation hours and coursework to their professional portfolio.
Prerequisites: PE 110
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
PE 289 - Lifeguarding
Credit Hours: 1
The purpose of this course is to provide participants with the knowledge and skills necessary to prevent, recognize and respond to aquatic situations and to provide professional-level care until emergency medical services (EMS) personnel take over. Successful completion of this course may lead to American Red Cross Lifeguarding certification. Prerequisites: 15 years old; excellent swim skills; swim test at first class: swim 300 yards continuously demonstrating breath control and rhythmic breathing, tread water for 2 minutes using only legs, and complete a timed event within 1 minute and 40 seconds.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the role and responsibilities of a professional rescuer;
- demonstrate the ability to implement an Emergency Action Plan (EAP) and perform assessments of an emergency; and
- demonstrate all ARC Lifeguarding, First Aid and CPR/AED-FPR skills.
S, SS (C)
|
| |
-
PE 290 - Lifeguarding Instructor
Credit Hours: 1
This instructor course is designed to train students to teach the American Red Cross Lifeguarding certification requirements and all of its subcomponents. Successful completion of this course may lead to American Red Cross Lifeguarding Instructor certification. Prerequisites: 17 years old; current Lifeguarding/FA; CPR/AED certification; pass 3 LGT final test skill scenarios/swim 300 yards; successfully complete Precourse-Online Session with American Red Cross.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- demonstrate characteristics required of an American Red Cross representative and role model;
- demonstrate knowledge of all American Red Cross Lifeguarding materials and all other information a Lifeguarding Instructor is qualified to teach;
- plan and conduct all the classes and modules encompassed in the courses a Lifeguarding Instructor is qualified to teach; and
- successfully demonstrate all skills encompassed in the classes a Lifeguarding Instructor is qualified to teach.
F/S, SS (C)
|
| |
|
Physics |
| |
-
PH 060 - Foundations in Science & Technology
Credit Hours: 3 Not for degree credit
This is an excellent course for the student taking developmental courses. It is recommended for students at the MT 013, MT 006, or MT 007 level. Through realworld applications, it provides relevant reinforcement that will enhance the learning process as well as provide a solid base for advanced science courses. Instruction will include but not be limited to exploring the following topics: physical problem solving, vectors with trigonometric analysis, graphing techniques, proportionality and dimensional analysis.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- explain and demonstrate some of the basic laws of nature;
- write comprehensive answers to qualitative questions;
- use elementary arithmetic or algebra to answer quantitative questions; and
- explain the physical laws pertain to technology, society and the environment.
Concurrent Registration: PH 061
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PH 061 - Lab for PH 060
Credit Hours: 1 Not for degree credit
This course is a hands-on companion laboratory designed to illustrate and enhance the lectures and activities in PH 060.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- explain and demonstrate some of the basic laws of nature;
- write comprehensive answers to qualitative questions;
- use elementary arithmetic or algebra to answer quantitative questions; and
- explain the physical laws pertain to technology, society and the environment.
Concurrent Registration: PH 060
F/S (N)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
PH 104 - Laser Uses in Society
Credit Hours: 3
An introduction to lasers and associated equipment for medicine, communications, industry, and military systems. A minimal background in algebra is needed to understand the nontechnical language which is a practical and easy-to-follow guide for beginners. By studying the conceptual drawings and tables the student will understand the applications of lasers.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- apply techniques of laser technology within the laboratory which mirror commercial uses;
- develop an understanding of the physical laws associated with lasers;
- develop an understanding of lasers applications; and
- explain how the optical behavior of light pertains to technology.
Prerequisites: MT 006
Corequisites: MT 007 or MT 013
F (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
PH 105 - Laboratory for Laser Uses in Society
Credit Hours: 1
An introduction to lasers and associated equipment for medicine, communications, industry, and military systems. A minimal background in algebra is needed to understand the non-technical language which is a practical and easy-to-follow guide for beginners. By studying conceptual drawings and tables, the student will gain an understanding of the applications of lasers.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- develop an understanding of the physical laws associated with lasers;
- develop an understanding of lasers applications;
- write precise technical laboratory reports; and
- explain how the optical behavior of light pertains to technology.
Prerequisites: MT 006
Corequisites: MT 007, MT 013
F (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
PH 124 - Earth Science I
Credit Hours: 4
A one-semester course designed to be taken in sequence with PH 125. PH 124 (lecture plus lab) introduces important geological processes that have environmental impacts, ranging from earthquakes and volcanic hazards to landslides and flooding. The framework for learning these processes will include the hydrologic cycle and the rock cycle. Discussions of environmental philosophy and the significance for society of the environmental findings of science will be covered. The laboratory involves hands-on experience with areas such as the following: field measurements of streams; map analysis; an examination of fossils as they relate to the environment; meteorite impacts; common rock-forming minerals; rocks; earthquakes; volcanoes; and soil classification.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- develop an understanding of the physical causes and events associated with natural earth processes; and
- develop an understanding of the current methods of monitoring, measuring, describing, predicting and reporting natural events.
F (C)
|
| |
-
PH 125 - Earth Science II
Credit Hours: 3
PH 125 offers an interdisciplinary discussion of both natural and human-induced global environmental change at various scales. The course provides a comprehensive description of how advances in the physical, biological and geological sciences are being integrated to understand the interplay between the Earth’s components (atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere). Topics include the Earth’s building blocks, the Earth through time, natural hazards, natural resources and Earth system cycles (such as weather, climate change and atmospheric pollution).
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- develop an understanding of the physical causes and events associated with natural earth processes; and
- develop an understanding of the current methods of monitoring, measuring, describing, predicting and reporting natural events.
S (C)
|
| |
-
PH 130 - Alternative Energy
Credit Hours: 3
This course is a non-math survey of our energy resources, options for future development and environmental impact of solar, nuclear, fossil fuels, wind and other alternatives. Practical ways to reduce energy use in the home and transportation will be considered along with methods of participating in decisions on energy policy and politics.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- explain the physical principles behind energy and its effects on the environment;
- identify and describe the dominant energy technologies;
- describe the status of energy resources, energy use and trends; and
- analyze simple problems involving energy concepts by using elementary arithmetic.
F/S (N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
-
PH 153 - Lab for PH 152
Credit Hours: 1
A required laboratory course to be taken concurrently with PH-152. Lab activities will correlate with the special topics covered in PH-152.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- collect experimental data using provided procedures in lab tasks;
- plan appropriate procedures to investigate a lab task; and
- interpret data using elementary mathematics and draw intelligent conclusions
|
| |
-
PH 157 - Interdisciplinary Approach to Structural Kinesiology
Credit Hours: 1
An introductory interdisciplinary course in structural kinesiology with laboratory applications in physics. This course is specifically intended for students in occupational therapy and may be taken by liberal arts science students interested in a kinesiology overview. Relationships between structure, function and the fundamental laws of physics will be emphasized. Topics include anatomical terminology, joint movement, measurements, linear motion, vectors, force, analysis of the bones, muscles and nerve innervations of the upper and lower extremities, rotational motion and basic biomechanics.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate the basic laws of nature;
- perform experiments to verify the laws of nature;
- apply mathematical skills and techniques to solve problems in nature; and
- read laboratory manuals and write precise technical laboratory reports.
F/S (N)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
Police Basic Training |
| |
-
PB 201 - Police Physical Fitness
Credit Hours: 3
Police Physical Fitness will provide students with diet and fitness information relevant to the functions of a healthy and active life. The students will be introduced to exercise programs that are specific to performing the job of law enforcement officers. The course will include a pre-test and post-test analysis of a three-segment program focused on push-ups, sit-ups and 1.5 mile run.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course participants will be able to:
- perform at or above the 50th percentile in the areas of muscular endurance and cardiovascular capacity;
- identify components of an exercise session and explain the reason for each; and
- identify activities at a personal physical fitness program that can be performed by an officer while off duty.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 202 - Basic Law for Police
Credit Hours: 3
Basic Law for Police will provide students an in-depth review of the New York State Penal Law. Emphasis will be placed on recognition, retention and understanding of the elements of offenses contained in the law. Instruction will also include a review of definitions, culpability and defenses.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- recognize the geographical jurisdiction of the offenses;
- identify types and jurisdictions of criminal courts;
- define criminal justice terminology;
- identify elements of an offense;
- identify levels of culpable mental states necessary for criminal responsibility;
- identify the difference between motive and intent; and
- identify the elements required for criminal responsibility.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 203 - Emergency Medical Services/First Responder
Credit Hours: 3
Emergency Medical Services/First Responder provides students the information relevant to immediate and temporary care given in cases of medical emergencies encountered by police officers. Medical emergencies and procedures will include communicable diseases, poisons, behavioral emergencies, injuries, burns, childbirth, splinting and CPR. Students will be responsible for passing the curriculum developed by the United States Department of Transportation.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- perform proper body substance isolations;
- initiate oxygen therapy utilizing the appropriate equipment;
- perform CPR;
- perform defibrillation and monitoring;
- assist in normal and abnormal obstetrical deliveries;
- identify the conditions in psychiatric emergencies;
- manage orthopedic emergencies to include splinting techniques; and
- manage violence containment.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 204 - Police/Community Relations
Credit Hours: 3
Police and Community Relations provides students with a blueprint for effective collaboration in crime prevention law enforcement, in concert with their eyes and ears, which is the community. The public relations advantages of close police/community bonds will be stressed as well as the concrete examples of combating crime through problem solving policing.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify and describe two needs of the victim;
- identify proper techniques for interacting with victims/witnesses;
- identify private and governmental organizations which offer referral services;
- identify situations where referral is appropriate and comprehend the proper way to refer an individual; and
- will be able to identify and explain the benefits of police/community collaboration.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 205 - Police Administration of Justice
Credit Hours: 3
Police and the Administration of Justice will provide the student with a comprehensive examination of the criminal justice system from the point of law enforcement. Components of the system to be examined will include the police, courts and corrections. Emphasis will be placed on the law enforcement role and the administrative responsibilities in each.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify the three major components of the criminal justice system;
- identify the seven major goals of the criminal justice system;
- identify the five primary goals of the law enforcement component;
- identify the four primary goals of the judicial component; and
- identify the four primary goals of the corrections component.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 206 - Police Arrest Techniques
Credit Hours: 3
Police Arrest Techniques provides students with information on developing and maintaining strong communications and human relations skills, using the force/levels of resistance matrix, searching and transporting prisoners and the mechanics of arrest. Demonstration skills and techniques will include the use of batons, aerosol sprays, methods of disarming, holds, handcuffing and protection against persons wielding deadly weapons.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify the elements and benefits of strong interpersonal and communication skills;
- identify the elements of the use of force/levels of resistance models and effectively demonstrate practical application;
- identify and practically apply proper stance and body movement;
- appropriate body language and verbal communication techniques;
- identify proper application and use of handcuffs;
- identify the appropriateness and applications of deadly force to lethal target areas; and
- identify the various types of person searches and comprehend the methods used.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 207 - Police Investigative Procedures
Credit Hours: 3
Police Investigative Procedures provides students with the opportunity and knowledge to identify, preserve, record, collect, store and transport physical evidence. Additionally the course will cover interviews and interrogations, focusing on approach, attitude, perceptions and evaluation of essential information.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify proper procedures for conducting preliminary investigations;
- define and identify sources of physical evidence;
- state the principles of processes in identifying, preserving, collecting, recording, storing, and transporting physical evidence;
- define interviews and interrogations;
- identify proper techniques for interviewing an individual; and
- list the goals and objectives of an interview.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 208 - Police Patrol Functions
Credit Hours: 3
Police Patrol Functions provides students the information to identify different types of patrol, including respective advantages and disadvantages of each. Preparation for patrol, determining the most effective patrol strategies, handling matters encountered while on patrol and factors which affect perception will be stressed. Instruction will also entail tactical procedures for responding to and handling crimes in progress.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify preventive patrol methods;
- identify the basic component of direct patrol;
- list the advantages and disadvantages of foot, bicycle, motorized patrol and horseback patrol;
- list the differences between preventive and apprehension patrol;
- identify vehicle patrol tactics which increase the effectiveness at crime detection; and
- identify basic patrol patterns.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 209 - Police Traffic Procedures
Credit Hours: 3
Police Traffic Procedures provides students with information relevant to traffic law enforcement. Topics will include recognizing and identifying elements of vehicle and traffic law offenses involving operator licensing, as well as vehicle registration, vehicle equipment, insurance requirements, vehicle operation and accident reporting.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- define traffic law enforcement;
- identify and define selective enforcement;
- identify actions an officer may take;
- list the steps involved in initial contact with a traffic violator;
- determine validity of driver information; and
- list procedures for completing and issuing traffic tickets.
F/S (N)
|
| |
-
PB 210 - Emergency Vehicle Operations
Credit Hours: 3
Emergency Vehicle Operations provides students with information relevant to instruction, demonstration and practical application elements of basic driving skills, as well as the legal principles common to law enforcement driving. Non-emergency and emergency response and pursuit will be stressed. The student will be made aware that violations of statutory and case law (as well as agency policy governing the various types of driving) can result in personal, criminal and civil liability.
Course Outcomes
After completing this course participants will be able to:
- identify statutory law, case law, agency policy and principles of liability governing emergency driving;
- identify constitutional law, statutory law and case law governing the use of vehicles as appropriate deadly force in terminating pursuits;
- identify reasons for law enforcement driver training;
- identify vehicle defects that contribute to law enforcement collisions;
- identify factors in route selection for emergency response;
- identify factors that impact on initiating a vehicle pursuit; and
- identify post litigation preparation considerations.
F/S (N)
|
Psychology |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
PS 102 - Positive Psychology: The Science of Happiness
Credit Hours: (3)
A one semester survey of the field of positive psychology, which studies happiness, how to define it and how to achieve it. The focus of the course will be on human strengths and virtues and how they help people and groups live fulfilling, pleasurable and meaningful lives. The course approach will be both empirical as well as experiential. Journal and essay writing, group exercises and experiential “homework” will be enlisted to both measure and help achieve the course goals. A service learning component is also recommended. Topics will include happiness, pleasure, positive and negative emotions, self-esteem, positive thinking, human strengths, virtue, values, goal setting, mind-body connections, relationships, emotional intimacy, health and wellness, resilience, religion and spirituality.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion, the student will be able to:
- analyze and interpret theory and research on achieving happiness and well-being, demonstrating a depth of knowledge of this subfield of psychology;
- demonstrate knowledge and understanding of concepts of happiness through written responses to questions derived from course readings;
- recognize valid determinants of happiness and well-being and show ability to distinguish these from invalid sources presented in popular culture;
- apply the psychological and physical interventions that according to research lead to a sense of personal well-being and happiness both during the course and after;
- understand through service-learning experience the link between service to others and personal well-being;
- use journal writing and meditation to achieve a better understanding of the self and to achieve a sense of well-bein; and
- work effectively in group exercises that apply course concepts in interactions with others.
F/S (C)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
Radiologic Technology-Radiation Therapy |
| |
-
RA 100 - Radiotherapy Technology I
Credit Hours: 3
During this course the student gains orientation to the principles underlying radiation therapy treatments, radiation oncology, professional ethics and duties of a radiation therapist. Appropriate handling of the radiation patient from clinical, ethical and technical points of view.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
-
prepare the radiation treatment room;
-
identify both machine and personnel radiation safety procedures;
-
differentiate between benign and metastatic neoplasms and identify their characteristics;
-
identify short term and long term radiation effects and tissue tolerances;
-
differentiate between various regulatory bodies; and
- explain patient rights and ethical conduct as a radiation therapist.
Corequisites: RA 101
F (C)
Three (3) 50-minute classes per week for 15 weeks.
|
| |
-
RA 101 - Lab/Clinical I
Credit Hours: 4
An orientation to the radiation departments of clinical affiliates. A clinical course designed to introduce students to basic radiotherapeutic procedures and equipment of radiation therapy. The student also is introduced to preparing treatment immobilization. The observation and clinical experiences of applying radiotherapy principles to patients under direct clinical supervision. Nursing procedures related to radiotherapy and basic radiation safety is also stressed.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this clinical, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate basic operation of the radiation treatment machine and bed;
- demonstrate interpersonal communication skills including compassion, caring and cultural awareness through verbal, nonverbal and written communication;
- assist the therapist in patient transport and treatment positioning;
- prepare the treatment room post and pre;
- identify and adhere to safety procedures for the patient, personnel, imaging equipment and treatment equipment;
- demonstrate comprehension of different imaging modalities/techniques and image matching following ALARA principles;
- develop and accurately label radiographic films (x-rays if applicable);
- provide basic patient care and assist in exam room procedures, patient follow-up, patient educational procedures for the radiotherapy patient; and
- identify clinical areas to improve and implement strategies to correct.
Corequisites: RA 100
F (C)
Two (2) eight-hour days per week; clinical rotations for 15 weeks. The first six (6) weeks will be conducted in the department’s lab, the remaining nine (9) will be held at affiliate sites.
|
| |
-
RA 102 - Lab/Clinical II
Credit Hours: 4
Students will participate in positioning and setting up the patient for the treatment procedure and producing custom shielding devices. Develop and label x-ray films/imaging plates (if applicable). Observing various imaging techniques and modalities. Students will rotate through the exam room and planning/simulation areas, as well as the treatment areas. During this course the student gains familiarity with and builds proficiency in the techniques, terms and tools used for radiation therapy treatments. The observation and clinical experiences of applying radiotherapy principles to patients under direct clinical supervision at all times.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this lab/clinical, the student will be able to:
-
create custom shielding and immobilization devices;
-
demonstrate how to correctly identify, assist and position the patient, pre/post treatment;
-
demonstrate ability to develop and accurately identify and label patient x-ray films/imaging plates (if applicable);
-
demonstrate proper use of the hand controls set machine and treatment bed parameters;
-
demonstrate safe and effective operation of the treatment and simulation machine and bed controls; and
-
evaluate the area of treatment and the radiation reactions.
Prerequisites: RA 101
Corequisites: RA 120
S (C)
Two (2) eight-hour days per week for 15 weeks.
|
| |
-
RA 120 - Radiotherapy Technology II
Credit Hours: 3
Designed to provide the student with a basic understanding of the following: medical terminology; radiographic imaging theory and methods; nutrition; emphasis on radiation therapy treatment planning; and dose calculations. Topics include quality assurance, treatment charts, alignment devices, and patient contours.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
-
describe the discovery and history of x-ray;
-
identify the components of an x-ray machine, cassette and intensifying screen;
-
list and describe the treatment and imaging modalities used in cancer management;
-
identify the components of tumor classification and staging system;
-
define such terms as: tissue tolerance, lethal dose, therapeutic ratio, fractionation, radiosensitivity, palliation, and isocenter;
-
state the content and purpose of the radiotherapy prescription;
-
distinguish between the three sources of radiation used for external beam radiation;
-
identify the components of a linear accelerator and their function; and
-
perform basic radiation therapy calculations.
Prerequisites: RA 100
Corequisites: RA 102
S (C)
Three (3) 50-minute classes per week for 15 weeks.
|
| |
-
RA 150 - Summer Clinical
Credit Hours: 6
During this course the student gains familiarity with and builds proficiency in the techniques, terms and tools used for radiation therapy treatments. The student also is introduced to preparing treatment immobilization devices and completion of calculation assignments.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
-
demonstrate ability to initiate and administer basic patient treatments;
-
demonstrate an understanding and explain use of treatment calculations;
-
demonstrate skill in assisting the physician/nurse with the patient in the exam room;
-
set and operate the machine and bed controls; and
-
identify and adhere to personal and equipment safety procedures.
Students will also begin to complete the required clinical and academic competencies consistent with those mandated by the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Prerequisites: RA 102, RA 120
SS (C)
Each rotation consists of six-hour days, five (5) days per week for the 12-week period.
|
| |
|
| |
-
RA 204 - Lab/Clinical IV
Credit Hours: 5
During this course the student attends various clinical affiliates for a period of 3 days per week for a total of 4-5 clinical rotations per semester, where they undergo supervised clinical experience.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
-
demonstrate proficiency in performing treatment calculations;
-
demonstrate the ability to immobilize and position a patient for CT simulation;
-
demonstrate the ability to apply patient set-up information and perform radiation treatments;
-
evaluate changes and corrections between acquired imaging and DRR’s; and
-
present a comprehensive patient case study.
*All clinical experiences are completely supervised.
Prerequisites: RA 203, RA 230
Corequisites: RA 240
S (C)
Two (2) eight-hour days, and one four-hour day, three days a week for the fifteen-week period.
|
| |
Page: 1 <- Back 10 … 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
| 12
| 13
| 14
| 15
|
|
|