|
|
2021-2022 Catalog [ARCHIVED CATALOG]
Course Descriptions
|
|
Key to Course Descriptions
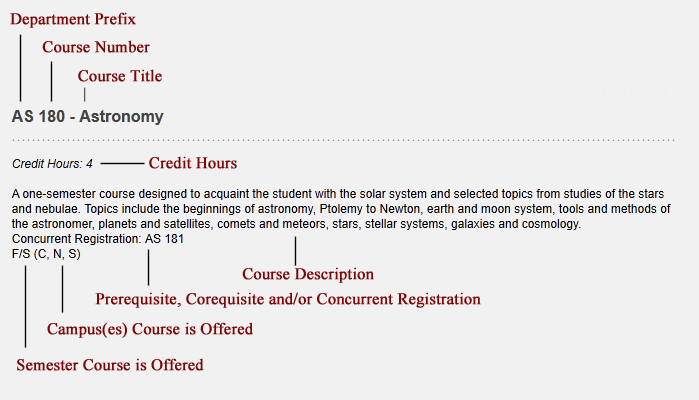
Abbreviations
| (C) |
City Campus |
F/S |
Fall and Spring |
| (N) |
North Campus |
SS |
Summer Session |
| (S) |
South Campus |
F+ |
Offered every other Fall |
| F |
Fall |
S+ |
Offered every other Spring |
| S |
Spring |
N |
Non-Credit |
Course Outlines
Course outlines for all courses described in this catalog are available for viewing. To explore the general framework of a course design and view the expectations of student performance within a select course click on the link below. These descriptions provide the base upon which instructors build their own course syllabi for the individual sections offered by the academic departments. Individual sections may therefore vary somewhat from the descriptions given in the outlines.
Course Outlines
|
| |
Automotive Technology |
| |
-
AU 123 - Ford ASSET Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical aspects of preventative maintenance, troubleshooting, overhaul and repair of Ford Motor Company automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- identify transmission/transaxle applications and types through the use of service manuals and codes. Competency will be base on lab performance and a practical test;
- demonstrate proper procedures for flushing transmission and/or transaxle cooling systems on Ford Motor Co. vehicles. Competency will be based on lab performance and activities;
- perform pressure test(s) and electrical scan tool checks for transmission/transaxle on Ford/L/M vehicles;
- completely disassemble, inspect and reassemble a RWD Transmission, FWD transaxle, both hydraulic and electronically controlled and show proper rebuilding procedures;
- demonstrate the proper OASIS and IDS diagnostic procedures related to Ford Motor Company automatic transmissions and transaxles;
- identify and show the proper use of the special tools, dial indicators, micrometers and feeler gauges needed to evaluate and overhaul automatic transmissions and transaxles. Competency will be based on lab activities; and
- perform internal and external adjustments as applicable to certain transmissions/transaxles. Competency will be based on lab activities and performance.
Concurrent Registration: AU 122
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 123 - Mopar CAP Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles Lab
Credit Hours: 2
The operation and diagnosis of automatic transmissions and transaxles on Dodge, Chrysler and Jeep vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
- research, test, and diagnose automatic transmission and transaxle problems;
- properly and safely remove and replace a transmission;
- research, disassemble, evaluate, and overhaul an automatic transmission;
- utilize the special tools required for transmission rebuilding; and
- application of the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler vehicles equipped with automatic transmission/transaxle. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 122
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 124 - Ford ASSET Manual Transmissions and Transaxles
Credit Hours: 2
A study of Ford manual transmissions/ transaxles. Topics to include clutches, drivelines, differentials, theoretical and practical aspects of maintenance, troubleshooting and overhaul procedures.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- identify clutch systems components. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify manual transmission and transaxle Powerflow Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify external component location on manual transmissions and transaxles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify component location of all parts located in the differential in either the front or rear of a Ford/L/M automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on activities in both the classroom/lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- identify the components related to the transfer case, driveshaft and CV joint repair and maintenance. Competency is based on both classroom and lab activities plus a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 125
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 124 - Mopar CAP Manual Transmissions and Transaxle
Credit Hours: 2
A study of manual transmissions, transaxles, transfer cases, and differentials. Topics include clutches, drivelines, theoretical and practical aspects of maintenance, trouble-shooting and overhaul procedures on Chrysler automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify clutch systems components. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify manual transmission and transaxle powerflow. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify external component location on manual transmissions and transaxles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify component location of all parts located in the differential in either the front or rear of a DaimlerChrysler automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on activities in both the classroom/lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- identify the components related to the transfer case, driveshaft and CV joint repair and maintenance. Competency is based on both classroom and lab activities plus a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 125
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 125 - Ford ASSET Manual Transmissions and Transaxles Lab
Credit Hours: 2
The practical application of lecture topics pertaining to the identification, overhaul and maintenance of manual transmissions and transaxles, differentials and transfer cases. Topics to include clutches, drivelines, theoretical and practical aspects of maintenance, troubleshooting and overhaul procedures.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- perform clutch diagnosis and bleeding procedure for hydraulic clutch assembly. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a score of at least 65%;
- disassemble and reassemble a transmission and a transaxle for a Ford Motor Co. vehicles. All end play and turning torque measurements are to be taken and recorded. Competency will be determined on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- disassemble and reassemble a transfer case and check all specifications as outlined in the Ford Motor Co. service manual. Competency will be based on competency in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- diagnose and repair a driveshaft and a CV joint on a vehicle with noise, vibration and harshness. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with grade of at least 65%; and
- application of the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford Motor Co. vehicles equipped with manual transmission/transaxle. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 124
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 125 - Mopar CAP Manual Transmission and Transaxle Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture including the identification, overhaul and maintenance of manual transmissions and transaxles, differential and transfer cases. Topics to include clutches, drivelines, theoretical and practical aspects of maintenance, troubleshooting and overhaul procedures related to Chrysler vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- perform clutch diagnosis and bleeding procedure for hydraulic clutch assembly. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a score of at least 65%;
- disassemble and reassemble a transmission and a transaxle for a Chrysler vehicles. All end play and turning torque measurements are to be taken and recorded. Competency will be determined on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- disassemble and reassemble a transfer case and check all specifications as outlined in the Chrysler service manual. Competency will be based on competency in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- diagnose and repair a driveshaft and a CV joint on a vehicle with noise, vibration and harshness. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with grade of at least 65%; and
- application of the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler vehicles equipped with manual transmission/transaxle. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 124
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 128 - Mopar CAP Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous CAP courses, taught with a Chrysler emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- determine through diagnosis problems related to the engine;
- use test equipment to determine the parts and/or related components requiring repair or replacement;
- disassemble/inspect/repair and reassemble all Chrysler 4-, 6-, 8-cylinder engines (recent production);
- disassemble major engine components for adjustment, repair or replacement;
- perform replacement of external components such as water pumps, valve covers/gaskets, oil pan/gaskets, etc.;
- demonstrate a working knowledge and show the proper use of micrometers, torque wrench, dial indicators, etc.;
- remove and install and engine assembly and be able to disconnect/connect related hoses, cables and electrical connections;
- demonstrate a working knowledge of the Chrysler Onboard Diagnostic system (OBD II);
- demonstrate a basic knowledge of the Chrysler DRB III;
- show the ability to identify and locate the various sensors, potentiometers, etc. tied to computer related automobile operation;
- read and follow diagnostic charts designed to aid in locating and repairing computer related problems;
- show the ability to identify and use special tools needed to remove and install faulty computer related components. (EXAMPLE: special tool needed to replace oxygen sensor);
- demonstrate the ability to use a DVOM to test and determine whether a component is good/bad;
- repair processor and related wiring to Chrysler manufacturer specifications;
- roadtest a vehicle with diagnostic equipment attached to determine a drivability problem; and
- demonstrate a working knowledge of the Antilock Braking System(s) (ABS) used by Chrysler.
All Daimler-Chrysler CAP Co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade Technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Chrysler College Automotive Program (CAP).
Corequisites: AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 129 - Ford ASSET Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous ASSET courses, taught with a Ford emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- determine through diagnosis problems related to the engine;
- use test equipment to determine the parts and/or related components requiring repair or replacement;
- disassemble/inspect/repair and reassemble all Ford 4-, 6-, 8-cylinder engines (recent production);
- disassemble major engine components for adjustment, repair or replacement;
- perform replacement of external components such as waterpumps, valve covers/gaskets,oil pan/gaskets, etc.;
- demonstrate a working knowledge and show the proper use of micrometers, torque wrenches, dial indicators, etc.;
- remove and install and engine assembly and be able to disconnect/connect related hoses,cables and electrical connections, etc.;
- demonstrate a working knowledge of the Ford Onboard Diagnostic system (OBD II);
- demonstrate a basic knowledge of the Ford Integrated Diagnostic System (IDS);
- show the ability to identify and locate the various sensors, potentiometers, etc. tied to computer related automobile operation;
- read and follow diagnostic charts designed to aid in locating and repairing computer related problems;
- show the ability to identify and use special tools needed to remove and install faulty computer related components. (EXAMPLE: special tool needed to replace oxygen sensor);
- demonstrate the ability to use a DVOM to test and determine whether a component is good/bad;
- repair processor and related wiring to Ford manufacturer specifications;
- roadtest a vehicle with diagnostic equipment attached to determine a drivability problem; and
- demonstrate a working knowledge of the Antilock Braking System(s) (ABS) used by Ford Motor Company.
All Ford ASSET Coops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade Technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Ford Automotive Student Service Educational Training Program (ASSET).
Corequisites: AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 130 - Suspension, Alignment and Brakes
Credit Hours: 2
Theoretical and practical study of the steering, suspension and brakes systems of an automobile. Included will be the diagnosis, repair and servicing of the above systems. (AU course required for Auto Body Major.)
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the operation and function of the components of Non-servo & Duo-servo drum brake systems by naming the components and answering multiple choice, true/false questions and labeling a diagram on an exam;
- describe the operation and function of the components of fixed, floating and sliding disc brake caliper systems by answering multiple choice and/or true/false questions on an exam;
- understand the basic principles of hydraulics and how they apply to the operation and function of all the hydraulic components of the brake system. This includes the master cylinder, combination valve, ABS HCU, lines, hoses, calipers and wheel cylinders. An exam will be give with multiple choice and/or true false questions;
- understand terminology associated with automotive brake systems, wheels, tires and the principles of how a vehicle stops. Competency will be based on an exam with multiple choice and/or true/false questions;
- understand the terminology and concepts associated with steering, suspension and alignment of an automobile including but not limited to Camber, Caster, Toe, Steering Axis Inclination and Toe Out on turns and how they affect the stability of an automobile. Competency will be based upon an exam with multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank and short answer questions;
- understand the function and operation of front suspension systems and any applicable terminology. An exam will be given for competency with multiple choice and true/false questions;
- understand the function and operation of rear suspension systems and any applicable terminology. An exam will be given for competency with multiple choice and true/false questions; and
- describe the operation and function of the steering systems of automobiles. This will include but not be limited to conventional and rack and pinion steering gears; power steering pumps, hoses and lines; steering columns and four wheel steering. Competency will be based on an exam with multiple choice and true/false questions.
Concurrent Registration: AU 131
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 131 - Lab for Suspension, Alignment and Brakes
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics. Students will perform repair and adjustment of the steering, suspension and brake systems on modern automobiles and light trucks. (AU course required for Autobody Major.)
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- inspect a vehicles complete brake, steering and suspension system and determine condition of the components and if repair or replacement is necessary. A lab report and inspection form will be used to determine competency;
- repair a vehicles disc brake system. This will include but not be limited to the replacement of the brake pads, machining or replacement of the brake rotors, maintenance of the brake caliper and bleeding of the brake system. Competency will be based upon a student working in the lab and a lab report;
- repair a vehicles drum brake system. This will include but not be limited to the replacement of drum brake shoes, hardware, machining or replacement of the drums, adjustment of the parking brake and bleeding of the hydraulic system. The students will be assessed by their lab report and working in the lab;
- repair a vehicles hydraulic brake system. This could include but not be limited to master cylinder, disc brake caliper, wheel cylinder, ABS hydraulic control unit, lines and hoses. Competency will be based upon efforts in the lab and a written lab report;
- repair a vehicles wheel, tire and/or wheel bearing. This will include but not be limited to dismounting and mounting of a tire, repair of the tire, balancing of the assembly and the replacement or service to the wheel bearing. Lab work combined with a lab report will be used for assessment;
- repair the front and rear suspension of a vehicle. This could include the springs, shock absorbers, bushings, control arms ball joints or steering knuckles. Competency will be based on working in the lab and a lab report; and
- repair the steering system of a vehicle. This could include but not be limited to the repair or replacement of the steering gear, steering column, power steering pump, steering linkage and the alignment of all 4 wheels of the vehicle. Competency will be based on working in the lab and a lab report.
Concurrent Registration: AU 130
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 150 - Introduction to Automotive Technology
Credit Hours: 2
A study in the advancements in the automotive industry, use and maintenance of equipment, safety in the shop and introduction to automotive systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- have practical knowledge and understanding of safe shop procedures, precautions, and individual responsibilities associated with the right to know laws;
- identify the possible areas of employment within the automotive field, and utilize this information to determine a career objective;
- prepare an industry acceptable resume;
- explain the mission of the ASE, and the benefits of certification;
- visually identify various hand tools and shop equipment. Describe their proper use and required maintenance;
- demonstrate proper handling and usage of the oxy-acetylene torch;
- identify and categorize numerous fasteners used in the automotive trade areas;
- outline strategies and describe the various methods used for broken fastener extraction;
- access the available online information system to produce vehicle specific Information requested by the instructor; and
- locate manufacturer’s service schedules, explain their importance, and basically describe the procedures involved in very basic fluid maintenance.
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 160 - Automotive Electrical
Credit Hours: 2
A study of the electrical system found in the modern-day automobile. Topics include the use of diagnostic meters, starting, charging, lighting, and accessory systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the behavior of electricity including voltage, resistance, current and Ohm’s Law;
- demonstrate proper use of diagnostic meters;
- describe simple, series, parallel and series parallel circuits;
- describe the operation of various common electrical circuits;
- read and understand wiring diagrams;
- demonstrate a proven diagnostic procedure; and
- utilize shop references to identify circuits and their operation.
Concurrent Registration: AU 161
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 161 - Lab for Automotive Electrical
Credit Hours: 2
A practical application of the diagnosis and repair of the electrical system found in the modern-day automobile. Tasks include the use of diagnostic meters and other equipment to repair problems in the electrical system.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate proper use of diagnostic meters;
- diagnose and repair automotive electrical systems;
- evaluate automotive batteries, starting and charging systems;
- demonstrate proper battery service procedures;
- crimp, solder and heat shrink wiring and connectors;
- read and understand wiring diagrams;
- demonstrate a proven diagnostic procedure; and
- utilize shop references to identify circuits and their operation.
Concurrent Registration: AU 160
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 162 - Automotive Engines
Credit Hours: 2
A study of the automobile engine. Topics include theoretical operation, construction, practical repair and troubleshooting of the four-, six- and eight-cylinder internal combustion engine.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify the location and function of all components in an internal combustion engine. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 60%;
- using measuring devices to determine which components in an engine are defective and need to be replaced or repaired. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- understand repair procedures for machine shop functions related to the internal combustion engine. These include the reconditioning of crankshafts, connecting rods, cylinder heads and engine blocks. Competency will be based upon a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- using the service manuals the student will be able to explain the proper procedures to reassemble an engine OHV/OHC. This should include timing, torque specs. and any special/unique steps specific to that engine. Competency will be based upon a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 163
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 163 - Lab for Automotive Engines
Credit Hours: 2
A practical study of the automotive engine including measuring and machining of the components related to the overhaul of a modern four-, six-, eight- or 10-cylinder internal combustion engine.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- completely disassemble, inspect, measure, machine or replace all the internal components of an internal combustion engine. Testing prior to overhaul will include but not be limited to oil pressure, compression, and cylinder leak down. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- properly use all measuring devices as they apply to internal combustion engines. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- properly clean all components of an internal combustion engine and inspect for cracks or fatigue. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in an internal combustion engine. Competency will be based on activities in the lab.
Concurrent Registration: AU 162
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 170 - Automotive Brakes
Credit Hours: 2
Theoretical and practical study of the brake system. Areas covered include computerized brake systems, manual and power systems, drum and disc brakes, inspection and repair.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- understand the function of and proper repair of all components related to the operation of the disc brake systems. Competency will be based on a test with a score of at least 65%;
- understand the function and proper repair of all components related to the operation of the drum brake systems Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- understand proper measuring techniques for the measurement of rotor thickness, drum diameter and wheel hub run out with the usage of a dial indicator, drum micrometer and an outside micrometer. Competency will be based on a test and classroom activities with a grade of at least 65%;
- understand proper machining techniques for both brake drums and rotors including both on and off the vehicle equipment. Competency will be based upon work quality in the lab combined with a test for a score of at least 65%;
- understand the operation and diagnostic procedures of all components related to anti-lock and/or traction control systems on a given vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom activities combined with a test for a grade of at least 65%; and
- become proficient using the Star Scan, DRB III and the proper service manual to diagnose the anti-lock brake system on a given vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom activities combined with a test for a grade of at least 60%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 171
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 171 - Lab for Automotive Brakes
Credit Hours: 2
The practical application of the repair of the entire braking system on a modern automobile. Lab activities relate to the repair of mechanical, hydraulic, and electrical components
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- diagnose, inspect, remove and replace, rebuild, clean, adjust, test, and repair air conditioning and heating systems and components. The student will write a report for each required job task completed. To be considered correct, the report must follow the outline stated in the course evaluation;
- interpret manufacture’s manuals and specifications. The student will write up a report for each job task completed including the manufacturer’s procedures and specifications to be considered correct;
- select and use proper tools, equipment and materials needed to perform required job tasks. Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor and a written report by the student; and
- demonstrate the use of special equipment, such as the recovery/recycling/recharging station in the diagnosis and repairing of air conditioning systems and components. Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor.
Concurrent Registration: AU 170
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 172 - Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles
Credit Hours: 2
Theoretical and practical aspects of preventive maintenance, troubleshooting, overhaul and repair are covered.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- understand the fundamental operating principles of the automatic transmission and transaxle;
- research and identify specific transmissions and transaxles;
- identify other components and subsystems influencing the operation of the automatic transmission and transaxle;
- theoretically diagnose and repair problems affecting the performance of the automatic transmission and transaxle; and
- research and perform overhaul procedures on automatic transmissions and transaxles.
Concurrent Registration: AU 173
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 173 - Lab for Automatic Transmissions and Transaxles
Credit Hours: 2
The diagnosis and repair of an automatic transmission and transaxle. Electrical, mechanical and hydraulic problems will be diagnosed and the overhaul of an automatic transmission or transaxle will be performed.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- research, test, and diagnose automatic transmission and transaxle problems;
- properly and safely remove and replace a transmission;
- research, disassemble, evaluate, and overhaul an automatic transmission; and
- utilize the special tools required for transmission rebuilding.
Concurrent Registration: AU 172
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 174 - Manual Transmissions and Transaxles
Credit Hours: 2
A study of manual transmissions/ transaxles. Topics to include clutches, drivelines, differentials, theoretical and practical aspects of maintenance, troubleshooting and overhaul procedures.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- understand the fundamental operating principles of the manual transmission, transaxle, transfer case, differential, and clutch assembly;
- research and identify specific transmissions, transaxles, transfer cases, differentials, and clutch assemblies;
- identify other components and subsystems influencing the operation of the manual transmission and transaxle;
- theoretically diagnose problems affecting the performance of the manual transmission, transaxle, transfer case, differential, and clutch assembly; and
- research overhaul procedures on manual transmissions, transaxles, transfer cases, and differentials.
Concurrent Registration: AU 175
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 175 - Lab for Manual Transmissions and Transaxles
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics. Students will perform diagonsitic and repair procedures related the clutch, manual transmission or transaxle, differential and transfer cases on modern vehicles. They will also perform transmission, transaxle, transfer case and differential overhaul procedures.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
- develop a practical knowledge of the manual transmission, transaxle, transfer case, differential, and clutch assembly;
- research and identify specific transmissions, transaxles, transfer cases, differentials, and clutch assemblies;
- service components and subsystems influencing the operation of the manual transmission and transaxle;
- diagnose and repair problems affecting the performance of the manual transmission, transaxle, transfer case, differential, and clutch assembly; and
- perform overhaul procedures on manual transmissions, transaxles, transfer cases, and differentials.
Concurrent Registration: AU 174
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 212 - Ford ASSET Fuel and Emissions
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the fuel emission control systems as found on Ford Motor Company vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- describe 4/5 gas theory as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the operation and comparison of fuel injection systems as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper procedure for testing fuel and emission system components on Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford Motor Company fuel and emissions systems. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 212 - Mopar CAP Fuel and Emissions
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the fuel emission control systems as found on Chrysler vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- describe 5 gas theory as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the operation and comparison of fuel injection systems as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper procedure for testing fuel and emission system components on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler fuel and emissions systems. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 213 - Ford ASSET Fuel and Emissions Systems Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application and theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the fuel and emissions systems as found on Ford Motor Company vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- perform test to prove the effects of fuel and emission system function as it relates to 4 and 5 gas analyzers as it applies on Ford/L/M vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test the components related to the entire operation of fuel injection systems as they are found on Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- properly use service and diagnostic manuals to aid with the repair of Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
- perform the proper procedure for testing emission system components on Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on work performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford/Lincoln/ Mercury fuel and emission systems. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and classroom combined with a test for a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 213 - Mopar CAP Fuel and Emissions Systems Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the fuel and emissions systems as found on Chrysler vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- perform test to prove the effects of fuel and emission system function as it relates to 4 and 5 gas analyzers as it applies on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test the components related to the entire operation of fuel injection systems as they are found on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- properly use service and diagnostic manuals to aid with the repair of Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the proper procedure for testing emission system components on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on work performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler fuel and emission systems. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and classroom combined with a test for a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 215 - Ford ASSET New York State Inspection Lab
Credit Hours: 1
Conducting vehicle safety/emissions inspections according to New York State DMV guidelines.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- identify the requirements necessary to operate an approved NYS Inspection station, including space requirements, special tools, postings and all required paper work. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- individual requirements including work application process, work experience requirements, testing, and licensee duties as an inspector. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- types of vehicles required to be inspected and the different requirements for these vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the safety inspection on a vehicle to include service brake system, parking brake, tires, steering, suspension, front end, chassis, lighting and reflectors, windshield and other glass, mirrors, windshield wipers, horn, seat belts and fuel leaks. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform an emissions inspection on 1996 and newer vehicles including emissions inspection procedures, pre-emissions inspection safety check, effect of failure of OBD II low enhanced emission test, and emission control devices. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- issuance of certificates of inspection and inspection rejection notices and replacement of inspection stickers. Competency will be based on test(s) with a minimum grade of at least 65%;
- perform the required paperwork for ordering new inspection certificates, returning old certificates for credit, rejection certificates, replacement certificates, refunds and credit. Competency will be based on test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- set up and adjustment of headlamps as required using both headlamp aimers and the aiming screen. Including the replacement of aiming components as needed to properly perform the aiming tasks. Competency will be based on lab performance and evaluation.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 120, AU 121, AU 220, AU 221, AU 227, AU 228
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 215 - Mopar CAP New York State Inspection Lab
Credit Hours: 1
The current New York State inspection regulations and procedures. Safety and emissions procedures in regards to the inspection and testing of components related to state inspections.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify the requirements necessary to operate an approved NYS Inspection station including space requirements, special tools, postings and all required paper work. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- individual requirements including work application process, work experience requirements, testing, and licensee duties as an inspector. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- types of vehicles required to be inspected and the different requirements for these vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the safety inspection on a vehicle to include service brake system, parking brake, tires, steering, suspension, front end, chassis, lighting and reflectors, windshield and other glass, mirrors, windshield wipers, horn, seat belts and fuel leaks. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform an emissions inspection on 1996 and newer vehicles including emissions inspection procedures, pre-emissions inspection safety check, effect of failure of OBD II low enhanced emission test, and emission control devices. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- issuance of certificates of inspection and inspection rejection notices and replacement of inspection stickers. Competency will be based on test(s) with a minimum grade of at least 65%;
- perform the required paperwork for ordering new inspection certificates, returning old certificates for credit, rejection certificates, replacement certificates, refunds and credit. Competency will be based on test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- set up and adjustment of headlamps as required using both headlamp aimers and the aiming screen. Including the replacement of aiming components as needed to properly perform the aiming tasks. Competency will be based on lab performance and evaluation.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 120, AU 121, AU 220, AU 221, AU 227, AU 228
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 218 - Ford ASSET Engine Performance
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for theuse of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the ignition and engine control systems as found on the Ford Motor Co. automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of engine management systems as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify, locate and interpret the operation of the components used in the engine management systems as they apply to Ford Motor Co. vehicles. Competency will be based on test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for engine management and drivability concerns on Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems on Ford Motor Co. vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 218 - Mopar CAP Automotive Engine Performance
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the ignition and engine control systems as found on the Chrysler automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of engine management systems as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify, locate and interpret the operation of the components used in the engine management systems as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for engine management and drivability concerns on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 219 - Ford ASSET Engine Performance Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the ignition and engine control systems as found on Ford Motor Company automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify and test the operation of engine management systems as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify, locate and test the operation of the components used in Ford/Lincoln/Mercury ignition systems. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Ford/Lincoln/Mercury automobiles and light trucks. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a score of at least 65%;
- perform proper mechanical diagnostics to determine the internal condition of an internal combustion engine. These will include compression test (both wet and dry), cylinder leak down and the comparison of the results. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford Motor Co. engine performance areas. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 219 - Mopar CAP Automotive Engine Performance Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the ignition and engine control systems as found on Chrysler automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and test the operation of engine management systems as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify, locate and test the operation of the components used in Chrysler ignition systems. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Chrysler automobiles and light trucks. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test(s) with a score of at least 65%;
- perform proper mechanical diagnostics to determine the internal condition of an internal combustion engine. These will include compression test (both wet and dry), cylinder leak down and the comparison of the results. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler engine performance areas. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 220 - Ford ASSET Alignment and Suspension
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical applications for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the alignment and suspension system as found on the modern Ford Motor Company automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of front suspension systems as they are found on modern automobile and light trucks, including alignment and adjustment procedures. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of the rear suspension systems as they are found on the modern automobile and light truck, including alignment and adjustment procedures. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- understand the use of different spring construction and shapes including composite and tapered springs. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of the different types of steering systems as found on modern automobiles and light trucks. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of power steering systems and components as found on modern vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- understand test procedures for testing the proper operation of the power steering pumps and gear boxes. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities.
Concurrent Registration: AU 221
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 220 - Mopar CAP Automotive Alignment and Suspension
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the steering and suspension systems as found on modern Chrysler automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of front suspension systems as they are found on modern automobile and light trucks, including alignment and adjustment procedures. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of the rear suspension systems as they are found on the modern automobile and light truck, including alignment and adjustment procedures. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- understand the use of different spring construction and shapes including composite and tapered springs. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of the different types of steering systems as found on modern automobiles and light trucks. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation of power steering systems and components as found on modern vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- understand test procedures for testing the proper operation of the power steering pumps and gear boxes. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities.
Concurrent Registration: AU 221
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 221 - Ford ASSET Alignment and Suspension Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the useof modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the alignment and suspension systems as found on the modern Ford Motor Company automobile and light truck.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- completely remove and replace the entire front suspension and steering systems and perform a proper wheel alignment on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- completely remove and replace the entire rear suspension system and perform a proper wheel alignment on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test the power steering pump and steering gear for proper operation and leaks on a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a grade of at least 65%;
- perform a four wheel alignment on a modern vehicle that has an adjustable and a non-adjustable rear suspension. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a written test with a score of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the alignment and suspension area of a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 220
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 221 - Mopar CAP Automotive Alignment and Suspension Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application for the use of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing and servicing the alignment and suspension systems as found on modern Chrysler automobiles and light trucks.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- completely remove and replace the entire front suspension and steering systems and perform a proper wheel alignment on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- completely remove and replace the entire rear suspension system and perform a proper wheel alignment on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test the power steering pump and steering gear for proper operation and leaks on a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a grade of at least 65%;
- perform a four wheel alignment on a modern vehicle that has an adjustable and a non-adjustable rear suspension. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a written test with a score of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the alignment and suspension area of a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 220
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 222 - Ford ASSET Air Conditioning and Heating
Credit Hours: 2
Modern cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and repair of temperature control and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify the differences in air conditioning systems used on modern vehicles, including R-12, R-134a, type of drier and if an orifice tube or expansion valve. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the procedure for attaching manifold gauges to an air conditioning system and tell what proper pressure should be. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the function of all of the components in an air conditioning system. Competency will be based on a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation and testing of the control head on modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test and a score of at least 65%;
- understand the operation of the electrical parts of the air conditioning and heating system. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- understand and be able to perform test procedure on the cooling system of the vehicle as it relates to the heater system. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 223
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 222 - Mopar Automotive Air Conditioning and Heating
Credit Hours: 2
Modern cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and repair of temperature and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify the differences in air conditioning systems used on modern vehicles, including R-12, R-134a, type of drier and if an orifice tube or expansion valve. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the procedure for attaching manifold gauges to an air conditioning system and tell what proper pressure should be. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the function of all of the components in an air conditioning system. Competency will be based on a grade of at least 65%;
- identify and describe the operation and testing of the control head on modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test and a score of at least 65%;
- understand the operation of the electrical parts of the air conditioning and heating system. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- understand and be able to perform test procedure on the cooling system of the vehicle as it relates to the heater system. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 223
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 223 - Ford ASSET Air Conditioning and Heating Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Modern cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and the repair of temperature control and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- evacuate and recharge an air conditioning system. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- attach manifold gauges to a vehicle and determine the problem with the vehicle. Proceed to completely remove and replace all components in the heating and air conditioning system on the vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test and flush the cooling system of a modern vehicle. Included in the testing procedure is the quality of the coolant, temperature at which the thermostat opens and the cooling fan(s) turn on, and the flushing and recycling of the anti-freeze in the vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- using the computerized testing equipment, diagnose problems with the climate control system on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the air conditioning and heating areas of a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 222
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 223 - Mopar CAP Automotive Air Conditioning and Heating Systems Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Modern cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and the repair of temperature control and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- evacuate and recharge an air conditioning system. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- attach manifold gauges to a vehicle and determine the problem with the vehicle. Proceed to completely remove and replace all components in the heating and air conditioning system on the vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test and flush the cooling system of a modern vehicle. Included in the testing procedure is the quality of the coolant, temperature at which the thermostat opens and the cooling fan(s) turn on, and the flushing and recycling of the anti-freeze in the vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- using the computerized testing equipment, diagnose problems with the climate control system on a modern automobile or light truck. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the air conditioning and heating areas of a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on work performed in the lab and a test with a grade of at least 65%.
Concurrent Registration: AU 222
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 224 - Ford ASSET Computer Assisted Mechanisms
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical applications of computers in the control of functions on Ford Motor Company vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of computer controlled components as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of the Integrated Diagnostic System (IDS), OASIS and other diagnostic equipment as they apply to Ford Motor Company vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Ford Motor Co. vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for the engine management, fuel control and drivability concerns on Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- apply the SSCC diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford computer controlled systems. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the need for On Board Diagnostics II (OBD II) as it applies to Ford/Lincoln/Mercury and other manufacturers. Competency will be based on classroom activities and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper procedure for erasing codes on a OBD II vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities; and
- describe proper data recording procedures on Ford/Lincoln/Mercury vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom as well as a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 224 - Mopar CAP Computer Controlled Mechanisms
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical applications of computers in the control of functions on Chrysler vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the operation of computer controlled components as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of the Diagnostic Readout Box III (DRB III), the Mopar Diagnostic System (MDS) and other diagnostic equipment as they apply to Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for the engine management, fuel control and drivability concerns on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler computer controlled areas. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the need for On Board Diagnostics II (OBD II) as it applies to Chrysler and other manufacturers. Competency will be based on classroom activities and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- describe the proper procedure for erasing codes on a OBD II vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities; and
- describe proper data recording procedures on Chrysler vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom as well as a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 225 - Ford ASSET Computer Assisted Mechanisms Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application of computers in the control of functions on Ford Motor Company vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course the student will be able to:
- analyze and test the operation of computer controlled components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on performance in the lab combined with a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of the Integrated Diagnostic System (IDS), the Ford Oasis and other diagnostic equipment on Ford Motor Company and other vehicles.Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of modern vehicles. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for engine management, fuel control and drivability on a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- application of the SSCC procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Ford Motor Company computer controlled vehicle. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform diagnostic procedures on vehicles that have provisions for On Board Diagnostics II (OBD II). Competency will be graded on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the proper procedure for erasing codes on an OBD II vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom an lab activities; and
- perform proper data recording procedures on applicable vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the lab as well as a test(s) with a score of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 225 - Mopar CAP Computer Assisted Mechanisms Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical application of computers in the control of functions on Chrysler vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- analyze and test the operation of computer controlled components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on performance in the lab combined with a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of the Diagnostic Readout Box (DRB III), the Mopar Diagnostic System (MDS) and other diagnostic equipment on Chrysler and other vehicles. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate the proper use of service and diagnostic manuals used with the repair of modern vehicles. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- demonstrate a diagnostic strategy for engine management, fuel control and drivability on a modern vehicle. Competency will be based on performance in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- application of the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in Chrysler computer controlled vehicle. Competency will be based on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform diagnostic procedures on vehicles that have provisions for On Board Diagnostics II (OBD II). Competency will be graded on activities in the lab and a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the proper procedure for erasing codes on an OBD II vehicle. Competency will be based on classroom and lab activities; and
- perform proper data recording procedures on applicable vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the lab as well as a test(s) with a score of at least 65%.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111, AU 112, AU 113, AU 227, AU 228
Concurrent Registration: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 227 - Ford ASSET Automotive Electronics
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical study of the electronic systems in the modern automobile. Related to the operation of all computers and components and the proper repair of them.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the specific purpose and operation of input (sensing), control and output (load) devices. As they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify the general function of electronic controllers/computers as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify how specific electrical components interact within an electrical system. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test specific electrical components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in electrical circuits. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation inquestion and answer sessions.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111
Concurrent Registration: AU 228
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 227 - Mopar CAP Automotive Electronics
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical study of the electronic systems in the modern automobile. Related to the operation of all computers and components and the proper repair of them.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the specific purpose and operation of input (sensing), control and output (load) devices. As they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify the general function of electronic controllers/computers as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- identify how specific electrical components interact within an electrical system. Competency will be based on a test with a grade of at least 65%;
- test specific electrical components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in electrical circuits. Competency will be based on activities in the classroom with participation in question and answer sessions.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111
Concurrent Registration: AU 228
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 228 - Ford ASSET Automotive Electronics Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical study of the electronic systems in modern automobiles. Related to the operation of all computers and components and the proper diagnosis/repair.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the specific purpose and operation of input (sensing), control and output (load) devices as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- identify the general function of electronic controllers/computers as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- identify how specific electrical components interact within an electrical system. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- test specific electrical components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the electrical circuits. Competency will be based on activities in the lab.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111
Concurrent Registration: AU 227
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 228 - Mopar CAP Automotive Electronics Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Application of theoretical and practical study of the electronic systems in modern automobiles. Related to the operation of all computers and components and the proper repair of them.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- identify and describe the specific purpose and operation of input (sensing), control and output (load) devices as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- identify the general function of electronic controllers/computers as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- identify how specific electrical components interact within an electrical system. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%;
- test specific electrical components as they apply to modern vehicles. Competency will be based on work effort in the lab and a practical test with a score of at least 65%; and
- apply the six-step diagnostic procedure to diagnose and repair problems in the electrical circuits. Competency will be based on activities in the lab.
Prerequisites: AU 110, AU 111
Concurrent Registration: AU 227
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 238 - Mopar CAP Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous CAP courses, taught with a Chrysler emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- inspect the automobile heating system and related components to ensure proper operation;
- inspect the automobile air conditioning system and related components to ensure proper operation;
- inspect and where needed repair or replace heating or air conditioning components;
- following Chrysler procedures flush the cooling system and refill with proper coolant;
- following Chrysler procedures the student will evacuate/refill or charge the A/C system using approved refrigerant;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in diagnosis and repair of the air conditioning/heating system;
- roadtest a vehicle to assist in determining if a drivability problem is related to the steering or suspension systems;
- perform a pre-alignment inspection to determine if parts or components of the steering/suspension system need to be adjusted or replaced;
- properly replace worn or defective parts or components of the steering/suspension systems;
- replace tires and balance as required. Where necessary replace wheels that after testing prove to be defective;
- properly perform front wheel and, where needed, rear wheel alignments to correct drivability problems;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in the diagnosis and repair of problems associated to the suspension/steering systems;
- perform a New York State Inspection on a vehicle brought to the dealer for yearly inspection;
- perform the necessary repairs and adjustments as required by New York State Department of Motor Vehicles;
- write up the appropriate paperwork for a vehicle that has either passed or failed inspection; and
- demonstrate an understanding of the NYS Inspection manual and its contents as far as performing a proper and legal inspection.
All Chrysler CAP co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Chrysler College Automotive Program (CAP).
Corequisites: AU 215, AU 220, AU 221, AU 222, AU 223
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 239 - Ford ASSET Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous ASSET courses, taught with a Ford emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- inspect the automobile heating system and related components to ensure proper operation;
- inspect the automobile air conditioning system and related components to ensure proper operation;
- inspect and where needed repair or replace heating or air conditioning components;
- following Ford Motor Co. procedures flush the cooling system and refill with proper coolant;
- following Ford Motor Co. procedures the student will evacuate/refill or charge the A/C system using approved refrigerant;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in diagnosis and repair of the air conditioning/heating system;
- roadtest a vehicle to assist in determining if a drivability problem is related to steering or suspension systems;
- perform a pre alignment inspection to determine if parts or components of the steering/suspension system need to be adjusted or replaced;
- properly replace worn o defective parts or components of the steering/suspension systems;
- replace tires and balance as required. Where necessary replace wheels that after testing prove to be defective;
- properly perform front wheel and where needed rear wheels alignments to correct drivability problems;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in the diagnosis and repair of problems associated to the suspension/steering systems;
- perform a New York State Inspection on a vehicle brought to the dealer for yearly inspection;
- perform the necessary repairs and adjustments as required by New York State Department of Motor Vehicles;
- write up the appropriate paperwork for a vehicle that has either passed or failed inspection; and
- demonstrate an understanding of the NYS Inspection manual and it contents as far as performing a proper and legal inspection.
All Ford ASSET co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Ford Automotive Student Service Educational Training Program (ASSET).
Corequisites: AU 215, AU 220, AU 221, AU 222, AU 223
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 248 - Mopar CAP Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous CAP courses, taught with a Chrysler emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- change sparkplugs, sparkplug wires and other related ignition components;
- replace fuel, air and other filters that could affect the performance of the vehicles;
- repair or replace fuel line and fuel tank components when they malfunction;
- following Chrysler procedures to make sure that the engine is running properly;
- follow Chrysler procedures to make necessary engine adjustments;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in diagnosis and repair of the fuel and ignition systems;
- roadtest a vehicle to assist in determining if a drivability problem is related to the fuel, ignition or computer-assist system;
- perform diagnostic checks using the appropriate scan tool depending on year of vehicle; (DRB I, II, III)
- test and determine the condition of computer-related components and adjust or replace as required;
- test and determine the condition of the fuel injection and related components;
- as required do maintenance to fuel injection system to ensure proper performance; (this maintenance would be other than replacement of parts or filters)
- use Chrysler DRB III diagnostic system to help find drivability problems while on a roadtest; (requires two people)
- disassemble the fuel injection system and test individual components for a problem and replace as necessary injectors, fuel rail, throttlebody, pressure relief valve, etc.;
- check and repair or replace electrical connectors or wiring to meet manufacturer specifications;
- perform basic electrical tests to determine if a problem is related to the charging or starting systems or battery and not the computer system; and
- diagnose problems in the different systems by using Chrysler service manuals or software.
All Chrysler CAP co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Chrysler College Automotive Program (CAP).
Corequisites: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 249 - Ford ASSET Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous ASSET courses, taught with a Ford emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- change sparkplugs, sparkplug wires and other related ignition components;
- replace fuel, air and other filters that could affect the performance of the vehicles;
- repair or replace fuel line and fuel tank components when they malfunction;
- following Ford Motor Co. procedures to make sure that the engine is running properly;
- follow Ford Motor Co. procedures to make necessary engine adjustments;
- use appropriate service manuals/software to assist in diagnosis and repair of the fuel and ignition systems;
- roadtest a vehicle to assist in determining if a drivability problem is related to the fuel,ignition or computer-assist system;
- perform diagnostic checks using the appropriate scan tool depending on year of vehicle; (PDS or IDS)
- test and determine the condition of computer related components and adjust or replace as required;
- test and determine the condition of the fuel injection and related components;
- as required do maintenance to fuel injection system to ensure proper performance; (this maintenance would be other than replacement of parts or filters)
- use Ford Motor Co. IDS diagnostic system to help find drivability problems while on a roadtest; (requires two people)
- disassemble the fuel injection system and test individual components for a problem and replace as necessary. Injectors, fuel rail, throttlebody, pressure relief valve, etc.;
- check and repair or replace electrical connectors or wiring to meet manufacturer specifications;
- perform basic electrical tests to determine if a problem is related to the charging or starting systems or battery and not the computer system; and
- diagnose problems in the different systems by using Ford Motor Co. service manuals or software.
All Ford ASSET co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Ford Automotive Student Service Educational Training Program (ASSET).
Corequisites: AU 212, AU 213, AU 218, AU 219, AU 224, AU 225
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 258 - Mopar CAP Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous CAP courses, taught with a Chrysler emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course the student will be able to:
- roadtest vehicle to determine if there is a problem with the clutch or transmission/transaxle;
- adjust clutch linkage or adjust the shift linkage;
- remove the transmission/transaxle to replace the clutch assembly;
- disassemble the transmission/transaxle to replace worn or broken parts;
- follow DaimlerChrysler procedures to adjust clutch, adjust shift linkage, replace clutch or overhaul transmission/transaxle;
- drain and replace fluid in the transaxle or transmission;
- roadtest vehicle to determine if there is a problem with the automatic transaxle/transmission;
- perform diagnostic checks using the appropriate scan tool depending on year of vehicle; (DRB III)
- drain automatic transmission/transaxle and replace the screen. Refill the unit with the appropriate automatic transmission fluid and fill to the proper level;
- R&R automatic transmission or automatic transaxle;
- disassemble transmission/transaxle to determine problem and what is needed to correct problems;
- reassemble automatic transmission/transaxle installing new parts where needed;
- roadtest after repairs are made to make sure that all transmission/transaxle problems have been corrected; and
- diagnose and correct problems in the different transaxles/ transmissions by using DaimlerChrysler service manuals or software.
All Chrysler CAP co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Chrysler College Automotive Program (CAP).
Corequisites: AU 122, AU 123, AU 124, AU 125
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 259 - Ford ASSET Cooperative Work Experience
Credit Hours: 1.5
Theory and instruction received in previous ASSET courses, taught with a Ford emphasis, are applied to work in the sponsoring dealership.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- roadtest vehicle to determine if there is a problem with the clutch or transmission/transaxle;
- adjust clutch linkage or adjust the shift linkage;
- remove the transmission/transaxle to replace the clutch assembly;
- disassemble the transmission/transaxle to replace worn or broken parts;
- follow Ford Motor Co. procedures to adjust clutch, adjust shift linkage, replace clutch or overhaul transmission/transaxle;
- drain and replace fluid in the transaxle or transmission;
- roadtest vehicle to determine if there is a problem with the automatic transaxle/transmission;
- perform diagnostic checks using the appropriate scan tool depending on year of vehicle; (IDS or PDS)
- drain automatic transmission/transaxle and replace the screen. Refill the unit with the appropriate automatic transmission fluid and fill to the proper level;
- R&R automatic transmission or automatic transaxle;
- disassemble transmission/transaxle to determine problem and what is needed to correct problems;
- reassemble automatic transmission/transaxle installing new parts where needed;
- roadtest after repairs are made to make sure that all transmission/transaxle problems have been corrected; and
- diagnose and correct problems in the different transaxles/ transmissions by using Ford Motor Co. service manuals or software. (IDS or PDS)
All Ford ASSET co-ops are conducted with the student working with an “A” grade technician. All the above objectives would be performed under the guidance of a professional to aid the student in the learning process as well as ensuring that all repairs and inspections are performed properly and at the level expected of the manufacturer.
Prerequisites: Enrollment in the Ford Automotive Student Service Educational Training Program (ASSET).
Corequisites: AU 122, AU 123, AU 124, AU 125
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 260 - Alignment and Suspension
Credit Hours: 2
Modern testing techniques and the use of equipment for diagnosing servicing the steering and suspension systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- understand the terminology and concepts associated with steering, suspension and alignment of an automobile including but not limited to Camber, Caster, Toe, Steering Axis Inclination and Toe Out on turns and how they affect the stability of an automobile. Competency will be based upon an exam with multiple choice, true/false, fill in the blank and short answer questions;
- understand the function and operation of front suspension systems and any applicable terminology. An exam will be given for competency with multiple choice and true/false questions;
- understand the function and operation of rear suspension systems and any applicable terminology. An exam will be given for competency with multiple choice and true/false question;
- describe the operation and function of the steering systems of automobiles. This will include but not be limited to conventional and rack and pinion steering gears; power steering pumps, hoses and lines; steering columns and four wheel steering. Competency will be based on an exam with multiple choice and true/false question; and
- understand the function, operation and diagnosis of wheel bearings, wheels, tires, dynamic and static balance and the possible problems associated with them. Competency will be based on an exam with multiple choice and True/False questions.
Concurrent Registration: AU 261
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 261 - Lab for Alignment and Suspension
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics related to the repair of the steering and suspension systems on modern vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- inspect a vehicles complete steering and suspension system and determine condition of the components and if repair or replacement is necessary. A lab report and inspection form will be used to determine competency;
- repair a vehicles wheel, tire and/or wheel bearing. This will include but not be limited to dismounting and mounting of a tire, repair of the tire, balancing of the assembly and the replacement or service to the wheel bearing. Lab work combined with a lab report will be used for assessment;
- repair the front and rear suspension of a vehicle. This could include the springs, shock absorbers, bushings, control arms ball joints or steering knuckles. Competency will be based on working in the lab and a lab report; and
- repair the steering system of a vehicle. This could include but not be limited to the repair or replacement of the steering gear,steering column, power steering pump, steering linkage and the alignment of all 4 wheels of the vehicle. Competency will be based on working in the lab and a lab report.
Concurrent Registration: AU 260
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 262 - Automotive Fuel and Emissions
Credit Hours: 2
The usage of modern testing techniques and equipment for diagnosing and servicing of the fuel and emission systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- recognize the purpose and operation of components in the PCV, EVAP, AIR, CAT,EGR, emission control systems. The student is able to complete a 50-item multiple choice exam. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly;
- recognize the functions of an infrared exhaust gas analyzer as an inspection tool and efficient diagnostic tool. Identify which general problem areas could cause excessive HC and CO emissions . The student is able to complete a 50 item multiple choice exam on gas analysis. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly;
- understand the basic operation of themicroprocessor, the concept of closed-loop engine control, the necessity for precise control of air/fuel ratios and the operation of the oxygen sensor and other engine sensors. The student is able to complete a 50-item multiple choice exam on these topics. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly; and
- understand the operation of the fuel system, their components and types. To understand the manufacture’s diagnostic procedures and equipment needs. The student is able to complete a 50- item multiple choice exam on these topics. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly.
Concurrent Registration: AU 263
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 263 - Lab for Automotive Fuel and Emissions
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics. Diagnosis and repair of modern vehicle emission control systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student shouldbe able to:
- diagnose, inspect, remove and replace, rebuild, clean, adjust, test, and repair fuel and emission systems and components. The student will write a report for each required job task completed.To be considered correct, the report must follow the outline stated in the course evaluation;
- interpret manufacturer’s manuals and specifications. The student will write up a report for each job task completed including the manufacturer’s procedures and specifications to be considered correct;
- select and use proper tools, equipment and materials needed to perform required job tasks.Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor and a written report by the student listing tools and materials used; and
- demonstrate the use of special equipment, such as gas analyzers in the diagnosing and repairing of fuel and emission systems and components. Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor.
Concurrent Registration: AU 262
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 264 - Automotive Engine Performance
Credit Hours: 2
The usage of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing, servicing ignition systems and engine control systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the operation of the 4 stroke Otto cycle engine;
- describe the engine design factors that effect engine performance;
- describe the effect of atmospheric conditions on the operation of the engine;
- explain how cylinder conditions require adjustments of air/fuel ratio and ignition timing;
- describe the effects of compression on engine performance;
- describe the operation of various common ignition systems; and
- demonstrate a proven diagnostic procedure.
Concurrent Registration: AU 265
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 265 - Lab for Automotive Engine Performance
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics related to the usage of modern testing equipment and techniques for diagnosing, servicing ignition systems and engine control systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- diagnose and repair automotive engine systems including base-engine, ignition and exhaust;
- perform various diagnostic tests including compression, cylinder leakage, vacuum, cylinder balance and ignition analysis;
- retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes from various On-Board Diagnostic systems both OBD-1 and OBD-11 using both manufacturer and aftermarket scan tools
- read OBD data streams using both manufacturer and aftermarket scan tools including handheld and PC based tools;
- perform both manual and automated tests per the appropriate diagnostic flow chart;
- find and interpret shop manual information for both the diagnosis and repair of computer systems. This includes both printed and online repair information; and
- verify customer concerns and verify repairs.
Concurrent Registration: AU 264
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 266 - Service and Parts Management
Credit Hours: 3
Dealership operations such as personnel management, advertising, financial inventory and scheduling of work. Parts flow and managerial responsibility in the parts business.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the operation of a modern dealership;
- describe the operation of an independent repair shop; and
- describe the operation of a parts retailer.
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 267 - Automotive Technology Internship
Credit Hours: 3
The internship is designed to provide an experience within the automotive industry. Training will encompass the operations of retail repair businesses, wholesale and retail automotive parts suppliers, or fleet repair facilities. This work experience will prepare the student for employment in a modern technical workplace.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate appropriate methods of estimating and developing repair order/invoices;
- function efficiently in the daily tasks of the automotive industry;
- appreciate the necessity of punctual attendance of employees at a place of business; and
- promote effective communication within corporate entities.
Prerequisites: 2.5 GPA minimum, faculty recommendation.
F/S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 268 - New York State Inspection
Credit Hours: 1
The current New York State inspection regulations and procedures. Safety and procedures for testing components related to state inspections. Use of NYS CVIS System for computerized emission control testing.
Course Outcomes
Upon Completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- utilize the NYS Motor Vehicle Inspection manual to interpret NYS vehicle laws;
- identify and describe emission control systems pertaining to NYS inspection regulations;
- identify and describe all mechanical/electrical systemspertaining to NYS safety laws; and
- utilize NYS CVIS computer System.
Concurrent Registration: AU 269
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 269 - Lab for Automotive New York State Inspection
Credit Hours: 1
Performing the required repairs and test procedures on a vehicle so it will pass a New York State Vehicle Safety and Emission Inspection.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- identify the requirements necessary to operate an approved NYS Inspection station including space requirements, special tools, postings and all required paper work. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- individual requirements including work application process, work experience requirements, testing, and licensee duties as an inspector. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- types of vehicles required to be inspected and the different requirements for these vehicles. Competency will be based on a test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform the safety inspection on a vehicle to include service brake system, parking brake, tires, steering, suspension, front end, chassis, lighting and reflectors, windshield and other glass, mirrors, windshield wipers, horn, seat belts and fuel leaks. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- perform an emissions inspection on 1996 and newer vehicles including emissions inspection procedures, pre-emissions inspection safety check, effect of failure of OBD II low enhanced emission test, and emission control devices. Competency will be based on lab performance, worksheets and test(s) with a grade of at least 65%;
- issuance of certificates of inspection and inspection rejection notices and replacement of inspection stickers. Competency will be based on test(s) with a minimum grade of at least 65%;
- perform the required paperwork for ordering new inspection certificates, returning old certificates for credit, rejection certificates, replacement certificates, refunds and credit. Competency will be based on test(s) with a grade of at least 65%; and
- set up and adjustment of headlamps as required using both headlamp aimers and the aiming screen. Including the replacement of aiming components as needed to properly perform the aiming tasks. Competency will be based on lab performance and evaluation.
Concurrent Registration: AU 268
F (S)
|
| |
-
AU 270 - Air Conditioning and Heating
Credit Hours: 2
Modern cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and repair of temperature control and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- to understand the theory of operation, the basic components and system controls of automotive air conditioning and heating system. The student is able to compete a 50-item multiple choice exam. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly;
- the student will understand proper test procedures in establishing corrective diagnosis, relate basic system problems to the appropriate gauge readings and understand proper component service. The student is able to compete a 50-item multiple choice exam. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly; and
- the student will understand how reciprocating air conditioner compressors operate, know clutch components , various methods of oil checking and servicing. The student will also understand the environmental effects of escaped refrigerant and proper reclaiming and recycling according to state and federal laws. The student is able to complete a 50-item multiple choice exam. Acceptable performance will be 35 items answered correctly.
Concurrent Registration: AU 271
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 271 - Lab for Automotive Air Conditioning and Heating
Credit Hours: 2
Practical application of lecture topics related to cooling, heating and air conditioning. The diagnosing and repair of temperature control and air flow control of the heating and cooling systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student should be able to:
- diagnose, inspect, remove and replace, rebuild, clean, adjust, test, and repair air conditioning and heating systems and components. The student will write a report for each required job task completed. To be considered correct, the report must follow the outline stated in the course evaluation;
- interpret manufacture’s manuals and specifications. The student will write up a report for each job task completed including the manufacturer’s procedures and specifications to be considered correct;
- select and use proper tools, equipment and materials needed to perform required job tasks. Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor and a written report by the student; and
- demonstrate the use of special equipment, such as the Recovery/Recycling/Recharging Station in the diagnosis and repairing of air conditioning systems and components. Evaluation will be base on observation by instructor.
Concurrent Registration: AU 270
S (S)
See course descriptions of Automotive Technology courses including AU 130, AU 131, AU 160, AU 161, AU 270 and AU 271, all of which are required for the Automotive Trades/ Autobody Repair degree.
|
| |
-
AU 272 - Computer Assisted Mechanisms
Credit Hours: 2
The operation and diagnosis of computers controlling automobile operations. This includes Daimler Chrysler, Ford Motor Company, General Motors and other domestic vehicles as well as various import vehicle systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- describe the behavior of electricity including voltage, resistance, current and Ohm’s Law;
- describe the basic operation of a computer controlled system;
- identify and describe common computer system inputs;
- identify and describe common computer system outputs;
- describe diagnostic procedures including scan tool testing and manual testing; and
- utilize shop references to identify circuits and their operation.
Concurrent Registration: AU 273
S (S)
|
| |
-
AU 273 - Lab for Computer Assisted Mechanisms
Credit Hours: 2
The diagnosis and repair of computer-controlled automobile operations. This includes Chrysler, Ford Motor Company, General Motors and other domestic vehicles as well as various import vehicle systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- diagnose and repair automotive computer systems including powertrain control, body control, lighting control and various chassis control systems;
- diagnose and repair various network systems including SAE J1850 Pulse Width Modulated, SAE J1850 Variable Pulse Width, ISO 9141, ISO 14230 KWP2000, ISO 15765 Controller Area Network;
- retrieve Diagnostic Trouble Codes from various On-Board Diagnostic systems both OBD-1 and OBD-11 using both manufacturer and aftermarket scan tools;
- read OBD data streams using both manufacturer and aftermarket scan tools including handheld and PC based tools;
- perform both manual and automated computer system tests per the appropriate diagnostic flow chart. Test include manual scan tool testing and testing with handheld Digital Volt-Ohm Meters (DVOMs);
- find and interpret shop manual information for both the diagnosis and repair of computer systems. This includes both printed and online repair information; and
- verify customer concerns and verify repairs.
Concurrent Registration: AU 272
S (S)
|
Automotive Trades: Autobody Repair |
| |
-
AB 130 - Introduction to Autobody Repair
Credit Hours: 2
A study in the various topics of autobody repair, including safety, tools and equipment, vehicle designs and construction, paint systems and future technology.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should know:
-
safety and emergency procedures in regards to the Autobody environment;
-
the basic usage and maintenance of tools and equipment; and
-
a strong background in the environmental issues, vehicle designs, paint systems and future technology.
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 140 - Detailing
Credit Hours: 2
The total cleaning and upkeep of an automobile and its components. This will include the engine and luggage compartments and interior coverings as well as exterior finishes. Steam cleaning, proper use of an electric buffer, as well as compounding, color sanding and waxing of the exterior finish will be included in the course.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- demonstrate the proper use of tools and equipment;
- work safely with chemicals and products used;
- perform various detailing methods and procedures;
- properly restore on vehicles exterior and interior components with regards to designing and protection; and
- write a proper lab report.
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 150 - Autobody Skills I
Credit Hours: 2
Repair of minor body damage. Included will be the repair of dents and scratches, feather-edge sanding and the application of body fillers and undercoats.
Course Outcomes
At the completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- understand how to safely use tools and equipment;
- know the importance of anti-corrosion coatings and how they work;
- understand the procedures of using body filler, polyester putty, etc.;
- distinguish between the different primer classifications, thin applications and uses;
- understand the various methods of repairing sheet metal damages; and
- know the steps in repairing minor body damage.
Concurrent Registration: AB 151
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 151 - Autobody Skills I Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Repair of minor body damage. Included will be the repair of dents and scratches, feather-edge sanding and the application of body fillers and undercoats.
Course Outcomes
At the completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- repair minor body damage;
- apply and finish body filler;
- prepare for and apply anti-corrosion coatings; and
- write a proper lab report.
Concurrent Registration: AB 150
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 180 - Introduction to Welding Processes and Applications
Credit Hours: 3
This course will include theory and hands on aspects of modern welding methods. Included will be MIG, TIG, Arc/Stick and Oxyacetylene, as well as oxyacetylene and plasma arc cutting of different materials.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate the safe and proper use of welding equipment;
- perform welds with all of the equipment covered in this course;
- properly use the various cutting equipment; and
- demonstrate the proper use of tools associated with welding.
F (S)
This course cannot be used for the AAS degree in Automotive Trades/Autobody Repair.
This course can be used for the Industrial Technology Program and as an open elective for the Liberal Arts Program.
|
| |
-
AB 210 - Autobody Skills II
Credit Hours: 2
Repair of major damage. Included will be the repair of sheet metal damage, replacement of body sheet metal, plastic repair and the application of various undercoats in preparation for refinishing.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- understand how to safely use tools and equipment;
- know the importance of anti-corrosion coatings and how they work;
- understand the procedures of using body filler, polyester putty, etc.;
- distinguish between the different primer classifications, thin applications and uses;
- understand the various methods of repairing sheet metal damages; and
- know the steps in repairing minor body damage.
Concurrent Registration: AB 211
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 211 - Autobody Skills II Lab
Credit Hours: 3
Repair of minor damage. Included will be the repair of sheetmetal damage, replacement of body sheet metal, plastic repair and the application of various undercoats in preparation for refinishing.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- understand how to safely use tools and equipment;
- know the importance of anti-corrosion coatings and how they work;
- understand the procedures of using body filler, polyester putty, etc.;
- distinguish between the different primer classifications, thin applications and uses;
- understand the various methods of repairing sheet metal damages; and
- know the steps in repairing minor body damage.
Concurrent Registration: AB 210
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 230 - Frame & Unibody Construction & Repair
Credit Hours: 2
The analysis of damage including measuring, anchoring and pulling, straightening, stress relieving and replacement of structural components on both frame and unibody vehicles.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- analyze damage to both frame and unibody vehicles;
- measure and anchor a damaged vehicle;
- pull, straighten, and stress relieve the damage;
- replace structural components; and
- restore corrosion protection.
Concurrent Registration: AB 231
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 231 - Frame & Unibody Construction & Repair Lab
Credit Hours: 3
The analysis and repair of structural damage including measuring, anchoring and pulling, straightening, stress relieving, and replacement of structural components on both frame and unibody vehicles.
Course Outcomes
At the completion of this course, the student should be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- analyze damage to both frame and unibody vehicles;
- measure and anchor a damaged vehicle;
- pull, straighten, and stress relieve the damage;
- replace structural components; and
- restore corrosion protection.
Concurrent Registration: AB 230
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 232 - Body Welding
Credit Hours: 2
This course entails the use of MIG welding and plasma arc cutting as used in collision repair. The methods and procedures of restoring structural integrity when replacing welded components will be included along with the different types of welds and joints.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- proper and safe use of MIG welding equipment;
- the various weld types and their uses;
- the different weld joints and their applications;
- proper procedure of replacing structural components;
- procedures for working with High Strength Steel; and
- importance of restoration of structural integrity.
Concurrent Registration: AB 233
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 233 - Body Welding Lab
Credit Hours: 2
This course entails the use of MIG welding and plasma arc cutting as used in collision repair. The methods and procedures of restoring structural integrity when replacing welded components will be included along with the different types of welds and joints.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- properly setup and safely use a MIG welder and plasma arc cutter;
- perform various weld types;
- perform the different weld joints;
- properly replace welded body parts;
- properly replace structural components along with restoring structural integrity; and
- correctly work with high-strength steel used on today’s automobiles.
Concurrent Registration: AB 232
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 234 - Accessory Service & Repair
Credit Hours: 1
Service of all accessories on vehicles, including power windows, power locks, cruise control, power seats, automatic headlight dimmers, exterior and interior trim. ABS brakes and air bags will also be included.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- diagnosis, service, repair and install the accessories associated with the automobile;
- diagnosis and repair of Supplemental Restraint System; and
- diagnosis and repair of ABS Brakes Systems.
Concurrent Registration: AB 235
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 235 - Accessory Service Lab
Credit Hours: 2
Service on all accessories on vehicles, including power windows, power locks, cruise control, power seats, automatic headlight dimmers, exterior and interior trim. ABS brakes and air bags will also be included.
Course Outcomes
At the completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- use tools and equipment safely;
- diagnosis, service, repair and install the accessories associated with the automobile;
- diagnosis and repair of Supplemental Restraint System; and
- diagnosis and repair of ABS Brake Systems.
Concurrent Registration: AB 234
S (S)
|
| |
-
AB 240 - Refinishing
Credit Hours: 2
Techniques and procedures of paint application, single stage as well as two stage (base coat, clear coat) systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- know safety and emergency procedures in regards to automotive paints;
- know basic usage and maintenance of refinishing equipment; and
- have a strong fundamental background in the types of paint, the technique and procedures used and the problems and solutions associated with refinishing.
Concurrent Registration: AB 241
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 241 - Refinishing Lab
Credit Hours: 3
Techniques and procedures of paint application, single stage as well as two stage (base coat, clear coat) systems.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate appropriate methods of estimating and developing repair orders;
- demonstrate effective written and oral communication skills;
- demonstrate the proper use of tools; and
- demonstrate the application of multiple painting procedures.
Concurrent Registration: AB 240
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 242 - Estimating & Shop Management
Credit Hours: 3
Skills required to properly evaluate collision damage and repair, along with the procedures involved in writing a proper damage report and operation of the facilities will be included in this course.
Course Outcomes
At the completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- correctly assess vehicle damage;
- write an accurate and detailed damage report; and
- understand the principles of shop management.
F (S)
|
| |
-
AB 245 - Autobody Repair Shop Internship
Credit Hours: 3
This course will be an 8-hour per week in shop hands-on internship. All aspects and topics of autobody repair will be performed by the students.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- demonstrate safe working practices;
- perform pre-paint preparation procedures;
- refinish body panels using basecoat/clearcoat;
- repair minor body damage including metal straightening, body filler and application of undercoats in preparation for paint;
- repair plastic body parts;
- replace body parts;
- perform unibody/frame set-up, measurement and correction methods;
- perform various welds and weld joints;
- complete detailing of a paint finish including color sanding, buffing and polishing; and
- perform all other areas of collision repair required of any entry level autobody technician not mentioned above.
S (S)
|
Banking, Insurance, and Real Estate |
| |
-
BA 101 - Principles of Bank Operations
Credit Hours: 3
A fundamental course in commercial bank operations to give the banker a broad perspective of banking necessary for career development. Topics include banking in the economy, evolution of American banking, bank services, the deposit function, bank relationships with their depositors, check processing and collection, bank bookkeeping, teller functions, investments, trust departments and collections.
Course Outcomes
This course examines the role of commercial banks, savings institutions and credit unions in New York State, focusing on checking and savings accounts, credit and debit cards and loan philosophies and procedures. The role of the trust department is also considered.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BA 230 - Insurance I
Credit Hours: 3
A basic survey of the insurance business- introduction to fire insurance, inland marine, ocean marine, public liability insurance and the law of negligence, automotive insurance (no-fault) liability and physical damage.
Course Outcomes
This course covers a portion of the subject matter needed to sit for the NYS insurance broker’s exam.
F/S (C, N, S)
|
Biology |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
BI 107 - Human Biology
Credit Hours: 3
A science elective designed for non-science majors. Topics will include digestive system and nutrition, genetics and reproduction, nervous system and drugs and survey of disease.
Fulfills SUNY General Education – Natural Sciences.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
- INTRODUCTION TO HUMAN ORGANIZATION AND THE CELL
- describe the organization of life; and
- describe the role of the cell as the basic unit of structure and function.
- TISSUES/ORGAN SYSTEMS AND CONCEPT OF HOMEOSTASIS
- detail the four major types of tissues; and
- explain homeostasis and describe what happens if the body cannot maintain homeostasis.
- NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
- describe and distinguish each of the six nutrient classes based on structure, function and food sources;
- locate and detail the structures of the digestive system; and
- associate each structure with its digestive function, contrasting mechanical from chemical digestion where appropriate.
- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
- discuss the composition of blood, its formed elements and plasma;
- identify the major structures of the heart; describe their functions;
- differentiate between the three types of blood vessels; describe the functions of each; and
- describe the conduction system and cardiac cycle of the heart.
- NERVOUS SYSTEM, SENSE ORGANS, AND PSYCHOACTIVE DRUGS
- describe the basic structure of neurons and the mechanism of nerve impulse transmission;
- identify and characterize the subdivisions of the nervous system;
- locate and describe the functions of the major regions of the brain;
- compare and contrast the effects of subdivisions of the autonomic nervous system; and
- describe the structures and functions of selected sense organs.
- GENETICS AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
- describe the relationship of DNA, chromosomes, and genes; relate this to protein synthesis;
- define basic terminology of Mendelian genetics; apply these concepts to problem solving situations;
- explain selected genetic disorders in terms of chromosomal abnormalities; and
- detail the anatomy and physiology of the male and female reproductive systems and describe selected STDs.
- HEALTH RELATED ISSUES
- additional topics may include cancer, immunity, endocrine system, and respiratory system.
F/S (C, N, S)
This course does not satisfy the science requirement for liberal arts/science majors.
|
| |
|
| |
-
BI 109 - Laboratory for BI 107
Credit Hours: 1
A science elective for non-science majors to accompany BI 107, Human Biology. The lab will give students hands-on experience in use of the scientific method and common means of analysis used on the human body. This does not satisfy the lab science requirement for LAS Science majors.
Fulfills SUNY General Education – Natural Sciences.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
Scientific Method
- explain the process of the scientific method; and
- critically analyze examples of its use.
The cell and organelles
- recognize an animal cell; and
- identify the parts of a cell visible in the microscope.
Body organization
- identify the major body cavities and the organs contained in each; and
- be able to locate major organs of the integumentary, digestive, nervous, circulatory, muscular, respiratory, urinary, skeletal and reproductive systems.
Basic Chemistry
- discuss the role of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids in nutrition and body composition;
- determine pH using standard chemical tests; and
- observe changes due to osmosis and diffusion in a lab setting.
Microscopy and Measurements
- use metric measurement; and
- use a microscope and identify the function of each part
Tissues
- identify representative examples of the four major tissue groups; and
- name at least two organs and the tissues that comprise them.
Musculoskeletal System
- name some of the major bones of the body using a model; and
- identify a few of the major muscles from a dissection.
Nervous System and sense organs
- locate and describe the functions of the cerebrum, cerebellum, brain stem and diencephalon; and
- perform some tests that determine functioning of vision, hearing and touch.
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
- name and locate major structures of the heart;
- trace the pathway of blood through the heart;
- recognize the cells of the blood under a microscope; and
- record results of spirometry tests before, during and after exercise.
Digestive System and Nutrition
- list the organs of the alimentary canal and accessory organs giving their characteristics, location and function;
- assess personal nutritional patterns; and
- demonstrate an understanding of the importance of good nutrition in overall body health and disease prevention.
Reproductive System
- describe the anatomy and physiology of the male and female reproductive systems;
- discuss the male and female hormones and menstrual cycle; and
- examine chromosomes and conduct tests on DNA.
Concurrent Registration: BI 107
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
-
BI 112 - Biology II
Credit Hours: 3
A survey will be made of humans and other organisms to include the following systems: digestive, circulatory, respiratory, nervous and muscular systems. Animal behavior, evolution and ecology are also discussed. The ecology section will include the human relationship to the natural world and the effects of technology on the ecosystem.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
ANATOMICAL SYSTEMS
- describe the anatomy, physiology and primary pathologies of the major organ systems of man: respiratory, circulatory, digestive excretory, muscular and nervous; and
- describe the actions and side effects of commonly used/abused psychotropic drugs.
EVOLUTION
- explain the theory of evolution and state the evidence on which it is based;
- describe the five geological eras and the evolutionary changes associated with each;
- describe the theory and history of human evolution; and
- explain the evolutionary basis of ecology.
ECOLOGY AND POPULATION
- describe the interactions between organisms and between organisms and their environment: food chains, predator/prey relationships, mineral and nutrient cycles, ecological niches and soil building;
- describe the history of human population growth and the reasons for the population explosion;
- explain in detail the consequences of excessive population growth as it effects both developed and underdeveloped countries pollution control, resource management, energy production and food production; and
- explain problems associated with attempts to limit population growth in various countries.
Prerequisites: BI 110
F/S (C, N, S)
Lab BI 117 is recommended.
|
| |
-
BI 115 - Laboratory for BI 110
Credit Hours: 1
The laboratory will include physical and biochemical characteristics of cells, tissues, structure of plants and animals, genetics and DNA analysis.
Fulfills SUNY General Education – Natural Sciences.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- microscope: explain proper use and care of the compound microscope; including naming the parts, noting the functions and determining the diameter of field of a microscope;
- molecular models: construct molecular models and identify major biological molecules and functional groups of organic compounds;
- plant and animal cells: use models of cells and organelles to compare the anatomy of plant and animal cells;
- plant cells and tissues: examine and identify the major anatomical features of a plant root, leaf and stem; describe plant organelles (allow students an opportunity to gain first hand observations of these by making slides of an onion, elodea leaf, geranium leaf epithelium, and other living plant cells);
- animal cells and tissues: use slides of animal cells to study organelles in animal cells; identify twelve major tissues found in the body (noting the location of each) and make drawings labeling major parts of each tissue;
- physical aspects of life: perform experiments involving the processes of osmosis, diffusion and dialysis; graph the results of these experiments and draw conclusions;
- chemical aspects of life: perform and interpret results of chemical tests on biological molecules; explain the mode of action of the tests on chemical compounds;
- enzymes/cell respiration: study the effect of temperature, pH and concentration on enzyme activity;
- mitosis: differentiate plant versus animal cells during the various phases of mitosis;
- Mendelian genetics and corn: explain Mendelian laws of genetics including Mendelian ratios, outcomes of monohybrid and dihybrid crosses; be able to solve genetic problems and perform a Punnett square test and interpret results from data accumulated; and
- genetic fingerprinting: explain and apply DNA analysis via gel electrophoresis.
Concurrent Registration: BI 110
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
-
BI 117 - Laboratory for BI 112
Credit Hours: 1
The laboratory will deal with vertebrate anatomy and physiology. This will be followed by a study of fundamental ecological techniques.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the student will be able to:
- cardiopulmanary fitness: explain the implications of cardiopulmonary fitness and the techniques used to measure heart and lung functions;
- frog and pig disscection: name and recognize the external features and major muscles of the frog, the bones of the frog (and compare to the bones in a human skeleton) and name the internal organs and blood vessels of the frog; name and identify the external features of the head and neck, internal organs, blood vessels and reproductive systems of the fetal pig;
- shark and sheep dissection; physiology of the nervous system: identify features of the shark ear, sheep and shark eyes; compare and identify features of the shark, sheep and human brains; and
- bacteriology: demonstrate how to make a bacterial slide, smear, and Gram’s stain; identify the morphology of bacteria seen in the microscope and demonstrate how to test antibiotics against bacteria.
Concurrent Registration: BI 112
F/S (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
-
BI 124 - Western New York Flora
Credit Hours: 3
This course deals with plant taxonomy including plant collection, identification and herbarium preparation. Some work will be done in the lab and field trips will be arranged to nearby wilderness areas. This course does not satisfy the science requirement for liberal arts/ science majors.
Fulfills SUNY General Education – Natural Sciences.
Course Outcomes
Upon completion of the course, the student will be able to:
INTRODUCTION TO PLANT TAXONOMY
- define taxonomic terms;
- become familiar with the terms associated with the classification of plants; and
- explain interrelationship between allied sciences.
HISTORY OF PLANT CLASSIFICATION
- describe the history of plant classification;
- explain classification of plants based on habitat, numbers and phylogeny; and
- describe other contemporary systems.
PRINCIPLES OF TAXONOMY
- distinguish between major and minor categories of classification; and
- describe the morphological criteria used to determine taxonomy.
PHYLOGENETIC CONSIDERATIONS
- explain the significance of phylogeny to taxonomy;
- describe the phyletic concepts; and
- discuss contributions to phyolgenetic knowledge.
CURRENT SYSTEMS OF CLASSIFICATIONS
- describe the classification system developed by Bentham and Hooker;
- describe the classification system developed by Engler and Prantl; and
- describe the classification system developed by Benale, Weinstein, Pulle, Skottsberg, Besey, Haller and Hutchinson.
FIELD AND HERBARIUM TECHNIQUES
- Describe how to prepare a specimen for collection;
- Describe how to collect specimens;
- Explain how to store specimens; and
- Discuss how specimens are typed.
FIELD AND PLANT COLLECTIONS
- describe the various locations where field trips will be made to collect specimens including Zoar Valley, Botanical gardens, Bog/ecosystems, Forest/ecosystems, Meadow/ecosystems; Sculpture Park - Ashford;
- discuss the plant identification procedures; and
- explain the final stages of herbarium preparation.
HERBARIUM COLLECTION
- Collect 100 native plants; and
- Properly identify and label the collected plants including genus and species.
Concurrent Registration: BI 125
SS (C, N, S)
|
| |
|
| |
Page: 1
| 2
| 3
| 4
| 5
| 6
| 7
| 8
| 9
| 10
| 11
… Forward 10 -> 15 |
|
|